用FilterSecurityInterceptor对HttpServletRequest进行授权
| 本站(springdoc.cn)中的内容来源于 spring.io ,原始版权归属于 spring.io。由 springboot.io - Spring Boot中文社区 进行翻译,整理。可供个人学习、研究,未经许可,不得进行任何转载、商用或与之相关的行为。 商标声明:Spring 是 Pivotal Software, Inc. 在美国以及其他国家的商标。 |
|
|
本节在 Servlet架构和实现 的基础上,深入探讨了 authorization 在基于Servlet的应用程序中是如何工作的。
FilterSecurityInterceptor 为 HttpServletRequest 实例提供 authorization。它作为 Security Filter 之一被插入到 FilterChainProxy 中。
下图显示了 FilterSecurityInterceptor 的作用。
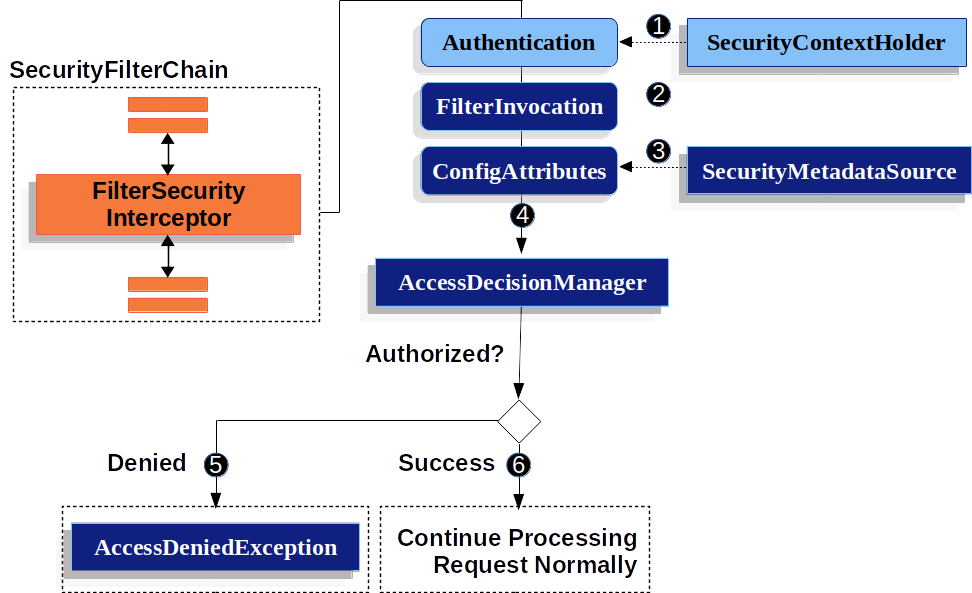
-

FilterSecurityInterceptor从 SecurityContextHolder 获得一个Authentication。 -

FilterSecurityInterceptor从传入FilterSecurityInterceptor的HttpServletRequest、HttpServletResponse和FilterChain中创建一个FilterInvocation。 -
 它将
它将 FilterInvocation传递给SecurityMetadataSource以获得ConfigAttribute。 -
 它将
它将 Authentication、FilterInvocation和ConfigAttribute传递给AccessDecisionManager。 -
 如果授权被拒绝,就会抛出一个
如果授权被拒绝,就会抛出一个 AccessDeniedException。在这种情况下,ExceptionTranslationFilter处理AccessDeniedException。 -
 如果访问被允许,
如果访问被允许,FilterSecurityInterceptor继续进行FilterChain,让应用程序正常处理。
默认情况下,Spring Security 的授权要求所有请求都要经过认证。下面的列表显示了明确的配置。
我们可以通过按优先顺序添加更多的规则(rule)来配置Spring Security的不同规则。
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
// ...
.authorizeRequests(authorize -> authorize (1)
.requestMatchers("/resources/**", "/signup", "/about").permitAll() (2)
.requestMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") (3)
.requestMatchers("/db/**").access("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')") (4)
.anyRequest().denyAll() (5)
);
return http.build();
}<http> (1)
<!-- ... -->
(2)
<intercept-url pattern="/resources/**" access="permitAll"/>
<intercept-url pattern="/signup" access="permitAll"/>
<intercept-url pattern="/about" access="permitAll"/>
<intercept-url pattern="/admin/**" access="hasRole('ADMIN')"/> (3)
<intercept-url pattern="/db/**" access="hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')"/> (4)
<intercept-url pattern="/**" access="denyAll"/> (5)
</http>@Bean
open fun filterChain(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
authorizeRequests { (1)
authorize("/resources/**", permitAll) (2)
authorize("/signup", permitAll)
authorize("/about", permitAll)
authorize("/admin/**", hasRole("ADMIN")) (3)
authorize("/db/**", "hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')") (4)
authorize(anyRequest, denyAll) (5)
}
}
return http.build()
}| 1 | 有多个授权规则被指定。每条规则都是按照它们的申报顺序来考虑的。 |
| 2 | 我们指定了多种URL模式,任何用户都可以访问。具体来说,如果URL以 "/resources/" 开头,等于 "/signup",或等于 "/about",任何用户都可以访问一个请求。 |
| 3 | A任何以"/admin/"开头的URL将被限制给拥有 "ROLE_ADMIN" 角色的用户。你会注意到,由于我们调用的是 hasRole 方法,我们不需要指定 "ROLLE_" 前缀。 |
| 4 | 任何以 "/db/" 开头的URL都要求用户同时拥有 "ROLE_ADMIN" 和 "ROLE_DBA"。你会注意到,由于我们使用的是 hasRole 表达式,我们不需要指定 "ROLE_" 前缀。 |
| 5 | 任何还没有被匹配的URL都会被拒绝访问。如果你不想意外地忘记更新你的授权规则,这是一个好的策略。 |
== 用 Dispatcher Type 配置 FilterSecurityInterceptor
默认情况下,FilterSecurityInterceptor 适用于每个请求。这意味着,如果一个请求是从一个已经被过滤的请求中派发出来的,FilterSecurityInterceptor 将对派发的请求执行同样的授权检查。在某些情况下,你可能不希望在某些调度器类型上应用授权。
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.dispatcherTypeMatchers(DispatcherType.ASYNC, DispatcherType.ERROR).permitAll()
.anyRequest.authenticated()
)
// ...
return http.build();
}<http auto-config="true">
<intercept-url request-matcher-ref="dispatcherTypeMatcher" access="permitAll" />
<intercept-url pattern="/**" access="authenticated"/>
</http>
<b:bean id="dispatcherTypeMatcher" class="org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.DispatcherTypeRequestMatcher">
<b:constructor-arg value="ASYNC"/>
<b:constructor-arg value="ERROR"/>
</b:bean>