Spring Boot 整合 QueryDSL 及常见用法
QueryDSL 是一个用于构建类型安全查询的开源 Java ORM 框架。它提供了一种 Fluent 风格的 API 来构建和执行数据库查询,并提供了编译时类型检查,以避免常见的查询错误。QueryDSL 支持多种数据库,包括关系型数据库和 NoSQL 数据库,可以与多个持久化框架(如 JPA、Hibernate 等)整合使用。它简化了查询的编写过程,使得查询代码更易于理解、维护和重用。
QueryDSL 在 Spring Boot 中通常配合 Spring Data JPA 使用,它会根据定义的 JPA Entity 类自动生成对应的查询类。通过查询类,除了可以快速地进行基本的 CRUD 操作外还支持 JOIN、GROUP、子查询等复杂的检索。而这一切都无需编写任何 SQL 语句,代码即 SQL。
本文将会带你了解如何在 Spring Boot 中整合 QueryDSL + Spring Data JPA,以及 QueryDSL 的常见用法。
示例项目
本文使用到的软件版本:
- Java:21
- Spring Boot:3.2.0
- MySQL:8.0.26
添加依赖
创建 Spring Boot 应用,完整的 pom.xml 如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springdoc-demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>21</java.version>
</properties>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>huaweicloud</id>
<url>https://mirrors.huaweicloud.com/repository/maven/</url>
<releases>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</releases>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- MYSQL 驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- JPA -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- QueryDSL JPA -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.querydsl</groupId>
<artifactId>querydsl-jpa</artifactId>
<version>${querydsl.version}</version>
<classifier>jakarta</classifier>
</dependency>
<!-- QueryDSL APT -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.querydsl</groupId>
<artifactId>querydsl-apt</artifactId>
<version>${querydsl.version}</version>
<classifier>jakarta</classifier>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>com.mysema.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>apt-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>process</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<outputDirectory>target/generated-sources/java</outputDirectory>
<processor>com.querydsl.apt.jpa.JPAAnnotationProcessor</processor>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
QueryDSL 的版本也受到 Spring Boot 的管理,因此在这里只需要将其版本号声明为 ${querydsl.version} 即可。
apt-maven-plugin Maven 插件的作用是根据 JPA Entity 生成查询类,其中 <outputDirectory> 节点指定了存放查询类的目录,而 <processor> 节点的配置则表示根据 JPA 注解生成查询类。
配置文件
在 application.yaml 中定义数据源和 JPA 等配置信息:
logging:
level:
"ROOT": INFO
# 输出 SQL 绑定参数
"org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind": TRACE
spring:
# 数据源
datasource:
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=GMT%2b8&allowMultiQueries=true
username: root
password: root
jpa:
# 输出 SQL
show-sql: true
properties:
# 格式化输出的 SQL
"hibernate.format_sql": true
如上,除了基本的数据源配置外。还配置了 org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind Logger 的日志级别为 TRACE,用于在日志中输出 SQL 绑定的参数。
Entity
定义一个 User 类,表示用户:
package cn.springdoc.demo.entity;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import jakarta.persistence.Column;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import jakarta.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "t_user")
public class User {
// ID
@Id
@Column
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
// 名称
@Column
private String name;
// 是否启用
@Column
private Boolean enabled;
// 创建时间
@Column
private LocalDateTime createAt;
// get、set、toString 方法省略
}
创建 Car 类,表示用户所拥有的汽车:
package cn.springdoc.demo.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Column;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import jakarta.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "t_car")
public class Car {
// ID
@Id
@Column
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
// 汽车名称
@Column
private String name;
// 用户 ID
@Column
private Integer userId;
// get、set、toString 方法省略
}
如上,使用 @Entity 注解表示该类是一个 JPA 实体类。该注解很重要,因为 QueryDSL 会根据此生成对应的查询类。
通过 @Table 注解指定表名称,通过 @Id 注解指定 ID 列,通过 @GeneratedValue 注解指定 ID 生成策略,这里使用的是 GenerationType.IDENTITY 即,使用数据库自增。通过 @Column 指定普通列。这都是很常见的 JPA 注解用法,这里不多解释。
一个 User 可以有多个 Car,这两个实体表示了一个一对多的关系。
对应的表结构如下:
-- User
CREATE TABLE `t_user` (
`id` int unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'ID',
`create_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`enabled` tinyint unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT '是否启用。0:禁用,1:启用',
`name` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '名字',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `name` (`name`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_general_ci COMMENT='用户';
-- Car
CREATE TABLE `t_car` (
`id` int unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'ID',
`name` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '汽车名称',
`user_id` int NOT NULL COMMENT '用户ID',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_general_ci COMMENT='汽车';
Repository
定义实体对应的 Repository 接口。
UserRepository:
package cn.springdoc.demo.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor;
import org.springframework.data.querydsl.QuerydslPredicateExecutor;
import cn.springdoc.demo.entity.User;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Integer>, JpaSpecificationExecutor <User>, QuerydslPredicateExecutor<User> {
}
CarRepository:
package cn.springdoc.demo.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor;
import org.springframework.data.querydsl.QuerydslPredicateExecutor;
import cn.springdoc.demo.entity.Car;
public interface CarRepository extends JpaRepository<Car, Integer>, JpaSpecificationExecutor <Car>, QuerydslPredicateExecutor<Car> {
}
除了基本的 JpaRepository 和 JpaSpecificationExecutor 接口外,Spring Data 还为 QueryDSL 提供了 QuerydslPredicateExecutor 接口,预定义了一些快捷的 CRUD 方法。
Application
最后,在 Application 类上添加 @EntityScan 和 @EnableJpaRepositories 注解,指定实体类和 Repository 接口所在的包。
package cn.springdoc.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
@SpringBootApplication
@EntityScan("cn.springdoc.demo.entity")
@EnableJpaRepositories("cn.springdoc.demo.repository")
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
至此,Spring Data JPA 和 QueryDSL 就整合完毕了。
你如果想了解整合 Spring Data JPA 的更多细节,你可以参考 这篇文章。
使用 QueryDSL
当你在项目中定义了实体类后,QueryDSL 其实已经偷偷为你生成了对应的查询类。
根据 pom.xml 中 apt-maven-plugin 插件的 <outputDirectory> 配置,查询类存放在 target/generated-sources/java 目录下。
本例中生成的查询类如下:
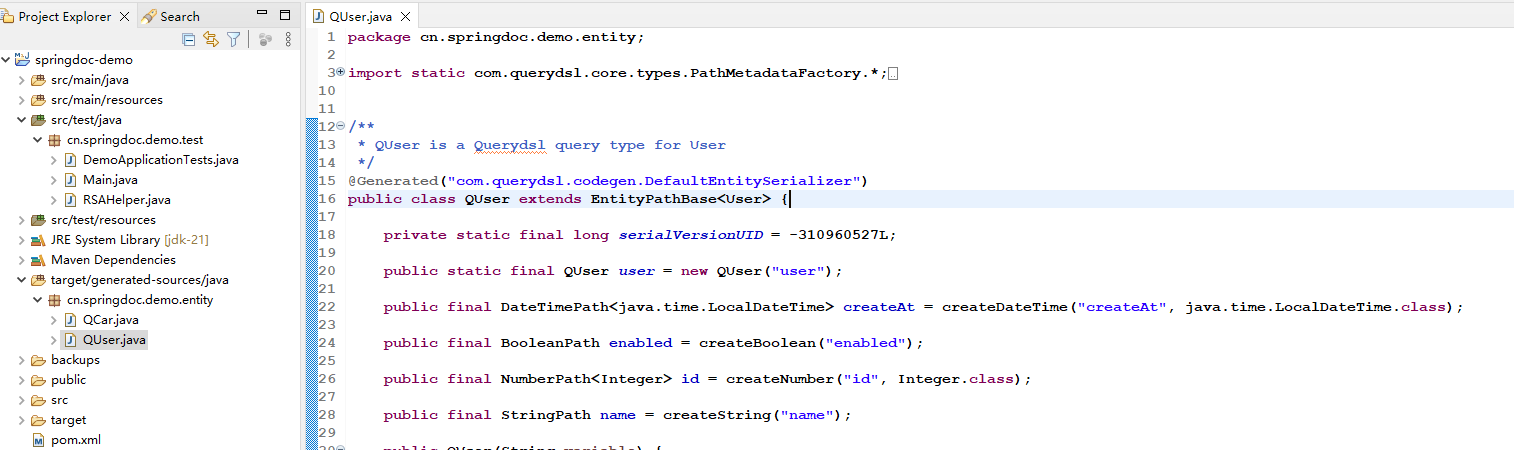
你可以看到,查询类以 Q 开头,名称对应实体类的名称。且包名和实体类所在包一样。最后打包的时候,这些查询类都会被打包到实体所在的包中。
在实际开发中,不建议修改自动生成的这些查询类。也不建议纳入版本控制,只要 Maven 配置正确,它们会自动生成。
自动生成的查询类,你不需要去研究太多。你只需要理解查询类中的每个字段,都对应了实体类以及数据表中的字段即可。
创建初始数据
QueyDSL 并未提供 INSERT 操作,我们需要依赖 Repository 的 save() 方法来保存实体。
插入测试数据:
package cn.springdoc.demo.test;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment;
import org.springframework.test.annotation.Rollback;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import cn.springdoc.demo.entity.Car;
import cn.springdoc.demo.entity.User;
import cn.springdoc.demo.repository.CarRepository;
import cn.springdoc.demo.repository.UserRepository;
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class DemoApplicationTests {
static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DemoApplicationTests.class);
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepository;
@Autowired
CarRepository carRepository;
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void test() throws Exception {
// 初始化 3 个用户
User u1 = new User(null, "刘备", Boolean.TRUE, LocalDateTime.now());
User u2 = new User(null, "张飞", Boolean.TRUE, LocalDateTime.now());
User u3 = new User(null, "关羽", Boolean.TRUE, LocalDateTime.now());
this.userRepository.save(u1);
this.userRepository.save(u2);
this.userRepository.save(u3);
// 给每个用户初始化 2 个 Car
this.carRepository.save(new Car(null, "宝马", u1.getId()));
this.carRepository.save(new Car(null, "奔驰", u1.getId()));
this.carRepository.save(new Car(null, "五菱", u2.getId()));
this.carRepository.save(new Car(null, "宝马", u2.getId()));
this.carRepository.save(new Car(null, "五菱", u3.getId()));
this.carRepository.save(new Car(null, "宝马", u3.getId()));
}
}
如上,创建了 3 个 User 对象,并给每个 User 创建了 2 个关联的 Car 对象。
执行测试。最终,数据表中的数据如下:
t_user:
| id | create_at | enabled | name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2023-12-10 16:01:55 | 1 | 刘备 |
| 2 | 2023-12-10 16:01:55 | 1 | 张飞 |
| 3 | 2023-12-10 16:01:55 | 1 | 关羽 |
t_cat:
| id | name | user_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 宝马 | 1 |
| 2 | 奔驰 | 1 |
| 3 | 五菱 | 2 |
| 4 | 宝马 | 2 |
| 5 | 五菱 | 3 |
| 6 | 宝马 | 4 |
基本的检索
检索单条记录和检索记录列表:
// 注入 EntityManager
@PersistenceContext
EntityManager entityManager;
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void test() throws Exception {
// 通过 EntityManager 创建 JPAQueryFactory 实例
var query = new JPAQueryFactory(entityManager);
QUser USER = QUser.user;
// 根据 id 和 enabled 检索单条记录
User user = query.selectFrom(USER).where(USER.id.eq(1).and(USER.enabled.eq(true))).fetchOne();
log.info("user={}", user);
// 检索集合
List<User> users = query.selectFrom(USER).where(USER.enabled.eq(true)).fetch();
log.info("users={}", users);
}
输出日志如下:
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.create_at,
u1_0.enabled,
u1_0.name
from
t_user u1_0
where
u1_0.id=?
and u1_0.enabled=?
TRACE 7028 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (1:INTEGER) <- [1]
TRACE 7028 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (2:BOOLEAN) <- [true]
INFO 7028 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : user=User [id=1, name=刘备, enabled=true, createAt=2023-12-10T16:01:55]
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.create_at,
u1_0.enabled,
u1_0.name
from
t_user u1_0
where
u1_0.enabled=?
TRACE 7028 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (1:BOOLEAN) <- [true]
INFO 7028 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : users=[User [id=1, name=刘备, enabled=true, createAt=2023-12-10T16:01:55], User [id=2, name=张飞, enabled=true, createAt=2023-12-10T16:01:55], User [id=3, name=关羽, enabled=true, createAt=2023-12-10T16:01:55]]
分页和排序
// 注入 EntityManager
@PersistenceContext
EntityManager entityManager;
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void test() throws Exception {
// 通过 EntityManager 创建 JPAQueryFactory 实例
var query = new JPAQueryFactory(entityManager);
QUser USER = QUser.user;
// 总记录数量
Long count = query.select(USER.id.count()).from(USER).fetchOne();
log.info("count={}", count);
// 分页 & 排序
List<User> users = query.selectFrom(USER).offset(0).limit(2).orderBy(USER.createAt.desc(), USER.id.asc()).fetch();
log.info("users={}", users);
}
执行日志如下:
Hibernate:
select
count(u1_0.id)
from
t_user u1_0
INFO 13836 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : count=3
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.create_at,
u1_0.enabled,
u1_0.name
from
t_user u1_0
order by
u1_0.create_at desc,
u1_0.id
limit
?, ?
TRACE 13836 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (1:INTEGER) <- [0]
TRACE 13836 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (2:INTEGER) <- [2]
INFO 13836 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : users=[User [id=1, name=刘备, enabled=true, createAt=2023-12-10T16:01:55], User [id=2, name=张飞, enabled=true, createAt=2023-12-10T16:01:55]]
投影查询
仅检索指定的列。
// 注入 EntityManager
@PersistenceContext
EntityManager entityManager;
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void test() throws Exception {
// 通过 EntityManager 创建 JPAQueryFactory 实例
var query = new JPAQueryFactory(entityManager);
QUser USER = QUser.user;
// 检索单列,单行
String name = query.select(USER.name).from(USER).where(USER.id.eq(1)).fetchOne();
log.info("name={}", name);
// 检索 id 和 name 列,封装结果为 Tuple
List<Tuple> tuples = query.select(USER.id, USER.name).from(USER).fetch();
tuples.stream().forEach(tuple -> {
log.info("id={}, name={}", tuple.get(USER.id), tuple.get(USER.name));
});
// 检索 id 和 enabled 列,通过 Setter 方法封装为实体
List<User> users = query.select(Projections.bean(User.class, USER.id, USER.enabled)).from(USER).fetch();
log.info("users={}", users);
}
执行测试,输出日志如下:
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.name
from
t_user u1_0
where
u1_0.id=?
TRACE 576 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (1:INTEGER) <- [1]
INFO 576 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : name=刘备
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.name
from
t_user u1_0
INFO 576 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : id=3, name=关羽
INFO 576 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : id=1, name=刘备
INFO 576 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : id=2, name=张飞
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.enabled
from
t_user u1_0
INFO 576 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : users=[User [id=1, name=null, enabled=true, createAt=null], User [id=2, name=null, enabled=true, createAt=null], User [id=3, name=null, enabled=true, createAt=null]]
JOIN 查询
JOIN 检索关联记录。
// 注入 EntityManager
@PersistenceContext
EntityManager entityManager;
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void test() throws Exception {
// 通过 EntityManager 创建 JPAQueryFactory 实例
var query = new JPAQueryFactory(entityManager);
QUser USER = QUser.user;
QCar CAR = QCar.car;
// INNER JOIN
List<Tuple> tuples = query.select(USER.id, USER.name, CAR.name.as("carName"))
.from(USER)
.innerJoin(CAR).on(CAR.userId.eq(USER.id))
.where(USER.enabled.eq(true))
.fetch()
;
tuples.stream().forEach(tuple -> {
log.info("userId={}, name={}, carName={}", tuple.get(USER.id), tuple.get(USER.name), tuple.get(CAR.name.as("carName")));
});
}
执行测试,输出日志如下:
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.name,
c1_0.name
from
t_user u1_0
join
t_car c1_0
on c1_0.user_id=u1_0.id
where
u1_0.enabled=?
TRACE 16652 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (1:BOOLEAN) <- [true]
INFO 16652 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : userId=1, name=刘备, carName=宝马
INFO 16652 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : userId=1, name=刘备, carName=奔驰
INFO 16652 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : userId=2, name=张飞, carName=五菱
INFO 16652 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : userId=2, name=张飞, carName=宝马
INFO 16652 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : userId=3, name=关羽, carName=五菱
INFO 16652 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : userId=3, name=关羽, carName=宝马
GROUP 查询
GROUP 聚合查询。
// 注入 EntityManager
@PersistenceContext
EntityManager entityManager;
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void test() throws Exception {
// 通过 EntityManager 创建 JPAQueryFactory 实例
var query = new JPAQueryFactory(entityManager);
QCar CAR = QCar.car;
// GROUP
List<Tuple> tuples = query.select(CAR.name, CAR.name.count())
.from(CAR)
.groupBy(CAR.name)
.fetch()
;
tuples.stream().forEach(tuple -> {
log.info("carName={}, count={}", tuple.get(CAR.name), tuple.get(CAR.name.count()));
});
}
执行测试,输出日志如下:
Hibernate:
select
c1_0.name,
count(c1_0.name)
from
t_car c1_0
group by
c1_0.name
INFO 8104 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : carName=宝马, count=3
INFO 8104 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : carName=奔驰, count=1
INFO 8104 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : carName=五菱, count=2
子查询
结果列子查询,以及条件语句中的子查询。
// 注入 EntityManager
@PersistenceContext
EntityManager entityManager;
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void test() throws Exception {
// 通过 EntityManager 创建 JPAQueryFactory 实例
var query = new JPAQueryFactory(entityManager);
QUser USER = QUser.user;
QCar CAR = QCar.car;
// 结果列子查询
List<Tuple> tuples = query.select(CAR.id, CAR.name,
JPAExpressions.select(USER.name).from(USER).where(USER.id.eq(CAR.userId)))
.from(CAR)
.fetch()
;
log.info("tuples={}", tuples);
// 条件子查询
List<User> users = query.selectFrom(USER)
.where(USER.id.in(JPAExpressions.select(CAR.userId).from(CAR).where(CAR.name.eq("宝马"))))
.fetch();
log.info("users={}", users);
}
执行测试,输出日志如下:
Hibernate:
select
c1_0.id,
c1_0.name,
(select
u1_0.name
from
t_user u1_0
where
u1_0.id=c1_0.user_id)
from
t_car c1_0
INFO 18848 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : tuples=[[1, 宝马, 刘备], [2, 奔驰, 刘备], [3, 五菱, 张飞], [4, 宝马, 张飞], [5, 五菱, 关羽], [6, 宝马, 关羽]]
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.create_at,
u1_0.enabled,
u1_0.name
from
t_user u1_0
where
u1_0.id in (select
c1_0.user_id
from
t_car c1_0
where
c1_0.name=?)
TRACE 18848 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (1:VARCHAR) <- [宝马]
INFO 18848 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : users=[User [id=1, name=刘备, enabled=true, createAt=2023-12-10T16:01:55], User [id=2, name=张飞, enabled=true, createAt=2023-12-10T16:01:55], User [id=3, name=关羽, enabled=true, createAt=2023-12-10T16:01:55]]
结果集封装
把结果集封装 Map,POJO 等。
// 注入 EntityManager
@PersistenceContext
EntityManager entityManager;
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void test() throws Exception {
// 通过 EntityManager 创建 JPAQueryFactory 实例
var query = new JPAQueryFactory(entityManager);
QUser USER = QUser.user;
QCar CAR = QCar.car;
// 结果集封装为 Map
List<Map<Expression<?>, ?>> ret = query.select(Projections.map(USER.id, USER.name, CAR.name)).from(USER)
.innerJoin(CAR).on(CAR.userId.eq(USER.id))
.fetch()
;
ret.stream().forEach(item -> {
log.info("userId={}, name={}, carName={}", item.get(USER.id), item.get(USER.name), item.get(CAR.name));
});
// 通过字段,封装为 Bean
List<User> users = query.select(Projections.fields(User.class, USER.id, USER.name)).from(USER)
.where(USER.id.in(1, 2))
.fetch()
;
log.info("users={}", users);
// 通过构造函数,封装为 Bean
User user = query.select(Projections.constructor(User.class, USER.id, USER.name, USER.enabled, USER.createAt)).from(USER)
.fetchFirst(); // fetchFirst 只检索结果集中的第一条记录
log.info("user={}", user);
}
执行测试,输出如下:
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.name,
c1_0.name
from
t_user u1_0
join
t_car c1_0
on c1_0.user_id=u1_0.id
INFO 17724 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : userId=1, name=刘备, carName=宝马
INFO 17724 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : userId=1, name=刘备, carName=奔驰
INFO 17724 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : userId=2, name=张飞, carName=五菱
INFO 17724 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : userId=2, name=张飞, carName=宝马
INFO 17724 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : userId=3, name=关羽, carName=五菱
INFO 17724 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : userId=3, name=关羽, carName=宝马
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.name
from
t_user u1_0
where
u1_0.id in (?, ?)
TRACE 17724 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (1:INTEGER) <- [1]
TRACE 17724 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (2:INTEGER) <- [2]
INFO 17724 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : users=[User [id=1, name=刘备, enabled=null, createAt=null], User [id=2, name=张飞, enabled=null, createAt=null]]
Hibernate:
select
u1_0.id,
u1_0.name,
u1_0.enabled,
u1_0.create_at
from
t_user u1_0
limit
?
TRACE 17724 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (1:INTEGER) <- [1]
INFO 17724 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : user=User [id=1, name=刘备, enabled=true, createAt=2023-12-10T16:01:55]
更新数据
QueryDSL 提供了更新数据的 API。
// 注入 EntityManager
@PersistenceContext
EntityManager entityManager;
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void test() throws Exception {
// 通过 EntityManager 创建 JPAQueryFactory 实例
var query = new JPAQueryFactory(entityManager);
QUser USER = QUser.user;
QCar CAR = QCar.car;
// 更新字段
long ret = query.update(USER)
.set(USER.name, "刘皇叔")
.set(USER.enabled, false)
.where(USER.id.eq(1))
.execute()
;
log.info("ret={}", ret);
// 子查询
ret = query.update(USER)
.set(USER.name, JPAExpressions.select(CAR.name).from(CAR).where(CAR.id.eq(1)))
.set(USER.enabled, true)
.where(USER.id.eq(8))
.execute()
;
log.info("ret={}", ret);
// 自增
ret = query.update(USER)
.set(USER.id, USER.id.add(-1))
.set(USER.enabled, true)
.where(USER.id.eq(9))
.execute()
;
}
执行测试,输出如下:
Hibernate:
update
t_user
set
name=?,
enabled=?
where
id=?
TRACE 13392 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (1:VARCHAR) <- [刘皇叔]
TRACE 13392 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (2:BOOLEAN) <- [false]
TRACE 13392 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (3:INTEGER) <- [1]
INFO 13392 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : ret=1
Hibernate:
update
t_user
set
name=(select
c1_0.name
from
t_car c1_0
where
c1_0.id=?),
enabled=?
where
id=?
TRACE 13392 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (1:INTEGER) <- [1]
TRACE 13392 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (2:BOOLEAN) <- [true]
TRACE 13392 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (3:INTEGER) <- [8]
INFO 13392 --- [ main] c.s.demo.test.DemoApplicationTests : ret=0
Hibernate:
update
t_user
set
id=(id+?),
enabled=?
where
id=?
TRACE 13392 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (1:INTEGER) <- [-1]
TRACE 13392 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (2:BOOLEAN) <- [true]
TRACE 13392 --- [ main] org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind : binding parameter (3:INTEGER) <- [9]
注意,本例中的 UPDATE 语句是不合理的(例如,ID 自增),这么写纯粹是为了演示 QueryDSL 的更新功能。
最后
QueryDSL 的用法总结:通过 EntityManager 创建 JPAQueryFactory 实例。然后使用查询类完成一系列的 CRUD 操作。
上述示例代码,基本上足够日常开发,但是如果业务中涉及的查询确实比较复杂,那么你可以考虑使用 Spring 6 中的 JdbcClient 来进行查询。
总结
本文介绍了如何在 Spring Boot 中整合 QueryDSL,以及 QueryDSL 的日常使用示例。
QueryDSL 是一款开发效率、灵活性、表达能力都非常高的 ORM。不用像 MyBatis 那样需要在 XML 中定义 SQL,再在 Mapper 接口中定义查询方法。

