工具(Tool)调用
| 本站(springdoc.cn)中的内容来源于 spring.io ,原始版权归属于 spring.io。由 springdoc.cn 进行翻译,整理。可供个人学习、研究,未经许可,不得进行任何转载、商用或与之相关的行为。 商标声明:Spring 是 Pivotal Software, Inc. 在美国以及其他国家的商标。 |
工具调用(亦称函数调用)是 AI 应用的常见模式,允许模型通过与一组 API(即工具)交互来扩展其能力。
工具主要应用于以下场景:
-
信息检索。此类工具可用于从外部源检索信息,例如数据库、网络服务、文件系统或网络搜索引擎。其目的是增强模型的知识,使其能够回答原本无法回答的问题。因此,它们可用于检索增强生成(RAG)场景。例如,可以使用工具检索给定位置的当前天气、检索最新新闻文章或查询数据库中的特定记录。
-
执行操作。此类工具可用于在软件系统中执行操作,例如发送电子邮件、在数据库中创建新记录、提交表单或触发工作流。其目的是自动化那些原本需要人工干预或显式编程的任务。例如,可以使用工具为与聊天机器人交互的客户预订航班、填写网页上的表单,或在代码生成场景中基于自动化测试(TDD)实现 Java 类。
尽管我们通常将工具调用称为模型能力,但实际上工具调用逻辑是由客户端应用程序提供的。模型只能请求工具调用并提供输入参数,而应用程序负责根据输入参数执行工具调用并返回结果。模型永远无法访问作为工具提供的任何 API,这是一个关键的安全考量。
Spring AI 提供了便捷的 API 来定义工具、解析模型的工具调用请求以及执行工具调用。以下部分概述了 Spring AI 中的工具调用功能。
| 请查阅 “聊天模型对比指南” 了解支持工具调用功能的 AI 模型清单。 |
| 请按照指南从已弃用的 FunctionCallback 迁移至 ToolCallback API。 |
快速入门
下面我们来看看如何在 Spring AI 中使用工具调用功能。我们将实现两个简单的工具:一个用于信息检索,另一个用于执行操作。信息检索工具将用于获取用户所在时区的当前日期和时间,而操作工具将用于设置指定时间的闹钟。
信息检索
AI 模型无法获取实时信息。任何需要知晓当前日期或天气预报等实时信息的问题,模型都无法直接回答。但我们可以提供能够检索这类信息的工具,当需要访问实时数据时,让模型调用这些工具。
下面我们在 DateTimeTools 类中实现一个获取用户所在时区当前日期时间的工具。该工具将不接收任何参数,通过 Spring Framework 的 LocaleContextHolder 获取用户时区信息。我们将使用 @Tool 注解来定义这个工具方法,并通过详细的工具描述帮助模型理解是否及何时调用该工具。
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.Tool;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
class DateTimeTools {
@Tool(description = "Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
String getCurrentDateTime() {
return LocalDateTime.now().atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId()).toString();
}
}接下来我们将该工具提供给模型使用。在本例中,我们将使用 ChatClient 与模型交互。我们将通过 tools() 方法传递 DateTimeTools 实例来向模型提供工具。当模型需要知道当前日期和时间时,它将请求调用该工具。在内部, ChatClient 将调用该工具并将结果返回给模型,模型随后将使用工具调用结果生成对原始问题的最终响应。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What day is tomorrow?")
.tools(new DateTimeTools())
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(response);输出结果如下:
Tomorrow is 2015-10-21.你可以再次提出同样的问题。这一次,不要向模型提供工具。输出结果如下
I am an AI and do not have access to real-time information. Please provide the current date so I can accurately determine what day tomorrow will be.如果没有这个工具,模型就不知道如何回答问题,因为它没有能力确定当前的日期和时间。
执行操作
AI 模型可用于生成实现特定目标的计划。例如,模型可以生成一个前往丹麦旅行的预订计划。但模型本身不具备执行计划的能力,这正是工具的用武之地:它们能执行模型生成的计划。
在前面的例子中,我们使用工具来确定当前的日期和时间。在本例中,我们将定义第二个工具,用于在特定时间设置闹钟。我们的目标是设置一个从现在开始 10 分钟的闹钟,因此需要向模型同时提供这两个工具来完成此任务。
我们将在之前的 DateTimeTools 类中添加这个新工具。该工具将接收一个 ISO-8601 格式的时间参数,并在控制台打印消息,提示已为指定时间设置闹钟。与之前一样,这个工具通过 @Tool 注解的方法定义,我们同样会提供详细描述,帮助模型理解何时及如何使用该工具。
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.Tool;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
class DateTimeTools {
@Tool(description = "Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
String getCurrentDateTime() {
return LocalDateTime.now().atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId()).toString();
}
@Tool(description = "Set a user alarm for the given time, provided in ISO-8601 format")
void setAlarm(String time) {
LocalDateTime alarmTime = LocalDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
System.out.println("Alarm set for " + alarmTime);
}
}接下来我们将这两个工具都提供给模型使用。我们将使用 ChatClient 与模型交互,通过 tools() 方法传入 DateTimeTools 实例来提供工具。当我们要求设置一个 10 分钟后的闹钟时,模型首先需要知道当前日期和时间,然后利用当前时间计算闹钟时间,最后使用闹钟工具设置闹钟。在内部,ChatClient 将处理模型发出的所有工具调用请求,并将工具执行结果返回给模型,使模型能够生成最终响应。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("Can you set an alarm 10 minutes from now?")
.tools(new DateTimeTools())
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(response);在应用程序日志中,你可以检查闹钟是否已在正确时间设置完成。
概览
Spring AI 通过一组灵活的抽象机制支持工具调用功能,这些抽象允许你以统一的方式定义、解析和执行工具。本节将概述 Spring AI 中工具调用的核心概念与组件构成。
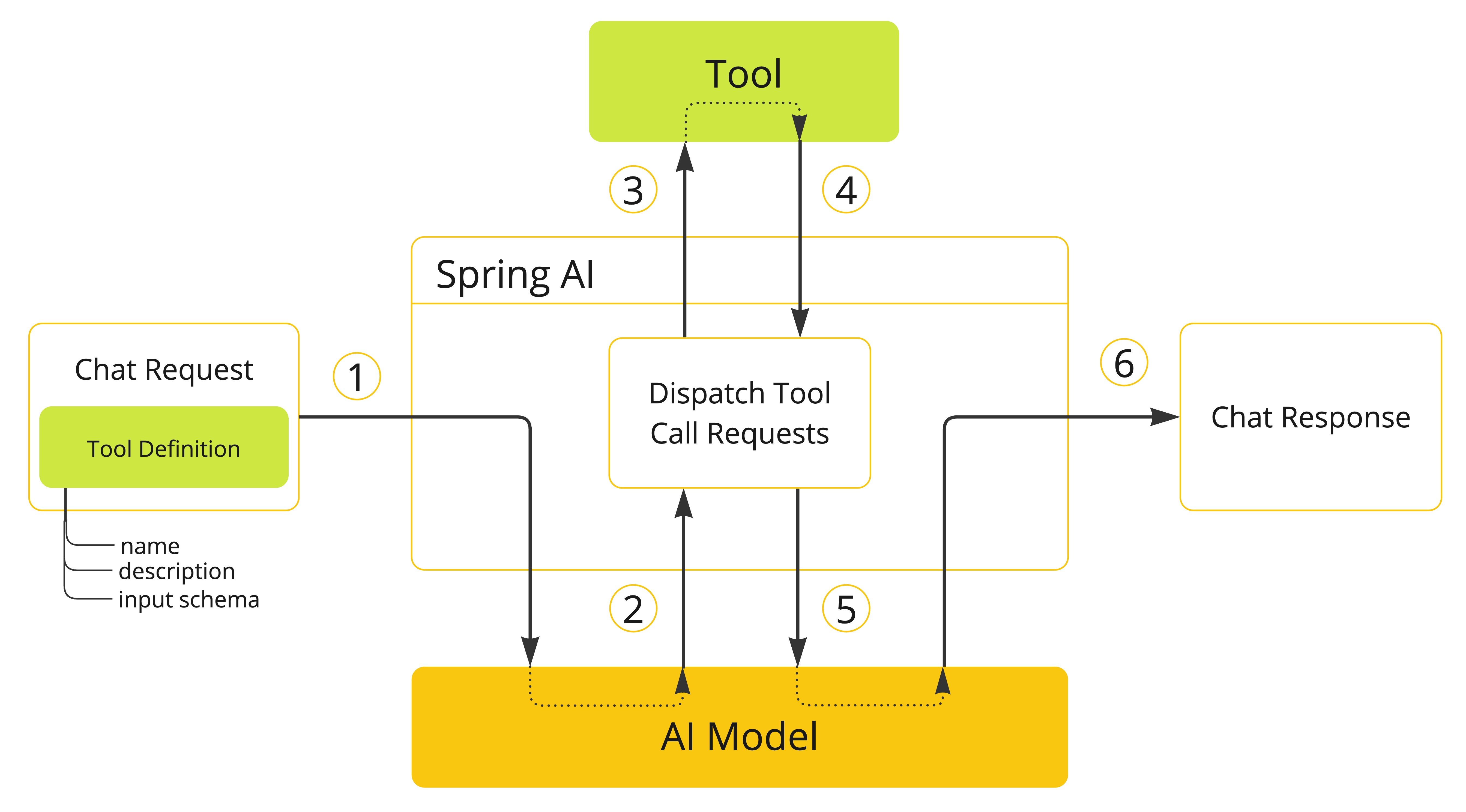
-
当我们想让模型使用某个工具时,我们会在聊天请求中包含该工具的定义。每个工具的定义都包括名称、描述和输入参数的模式。
-
当模型决定调用工具时,它会发送包含工具名称及符合预定义模式的输入参数的响应。
-
应用程序负责根据工具名称识别对应工具,并使用提供的输入参数执行该工具。
-
工具调用的结果由应用程序进行处理。
-
应用程序将工具调用结果返回至模型。
-
模型最终利用工具调用结果作为附加上下文生成响应。
Tool 是工具调用的基础构建单元,通过 ToolCallback 接口进行建模。Spring AI 内置支持从方法和函数生成 ToolCallback,同时你始终可以自定义 ToolCallback 实现以满足更多使用场景。
ChatModel 实现类会透明地将工具调用请求调度给对应的 ToolCallback 实现,并将工具调用结果返回模型以生成最终响应。该过程通过 ToolCallingManager 接口实现,该接口负责管理工具执行的完整生命周期。
ChatClient 和 ChatModel 均可接收 ToolCallback 对象列表,既向模型提供可用工具,也向最终执行这些工具的 ToolCallingManager 供支持。
除直接传递 ToolCallback 对象外,你还可传递工具名称列表,这些名称将通过 ToolCallbackResolver 接口进行动态解析。
以下章节将详细阐述这些核心概念与 API,包括如何通过定制化扩展来支持更多应用场景。
方法即工具
Spring AI 为方法转工具(即 ToolCallback)提供两种内置支持方式:
-
声明式:通过
@Tool注解实现。 -
编程式:通过底层的
MethodToolCallback实现。
声明式配置:@Tool 注解方案
你只需为方法添加 @Tool 注解,即可将其转换为工具。
class DateTimeTools {
@Tool(description = "Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
String getCurrentDateTime() {
return LocalDateTime.now().atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId()).toString();
}
}@Tool 注解允许你配置以下关键工具信息:
-
name:工具名称。若不指定,默认使用方法名称。AI 模型通过此名称识别调用工具,因此不允许在同一类中存在同名工具。模型处理单个聊天请求时,所有可用工具的名称必须保持全局唯一。 -
description:工具描述,用于指导模型判断何时及如何调用该工具。若未指定,默认使用方法名称作为工具描述。但强烈建议提供详细描述,因为这对模型理解工具用途和使用方式至关重要。若描述不充分,可能导致模型在该调用工具时未调用,或错误调用工具。 -
returnDirect:控制工具结果直接返回客户端(true)还是传回模型(false)。详见 [_return_direct] 章节说明。 -
resultConverter:用于将工具调用结果转换为字符串对象的ToolCallResultConverter实现,该字符串将返回至 AI 模型。详见结果 [_result_conversion] 章节说明。
该方法既可以是静态方法也可以是实例方法,并且可具有任意可见性(public、protected、package-private 或 private)。包含该方法的类既可以是顶级类也可以是嵌套类,同样支持任意可见性(只要在计划实例化的位置可访问即可)。
Spring AI 为使用 @Tool 注解的方法提供内置的 AOT(提前编译)支持,前提是包含这些方法的类必须是 Spring Bean(例如使用 @Component 注解)。否则,你需要为 GraalVM 编译器提供必要的配置,例如通过使用 @RegisterReflection(memberCategories = MemberCategory.INVOKE_DECLARED_METHODS) 注解标记该类。
|
你可以为方法定义任意数量的参数(包括无参数),支持大多数类型(基本类型、POJO、枚举、List、数组、Map 等)。同样,方法可以返回大多数类型,包括 void。若方法有返回值,则返回类型必须是可序列化类型,因为结果将被序列化并发送回模型。
| 部分类型不受支持,详见方法 [_method_tool_limitations] 章节说明。 |
Spring AI 将自动为 @Tool 注解方法的输入参数生成 JSON Schema。该 Schema 供模型理解如何调用工具及准备工具请求。你可使用 @ToolParam 注解为输入参数提供额外信息(如描述、是否必需等),默认情况下所有输入参数均为必需参数。
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.Tool;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.ToolParam;
class DateTimeTools {
@Tool(description = "Set a user alarm for the given time")
void setAlarm(@ToolParam(description = "Time in ISO-8601 format") String time) {
LocalDateTime alarmTime = LocalDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
System.out.println("Alarm set for " + alarmTime);
}
}@ToolParam 注解允许你配置工具参数的关键信息:
-
description:参数描述,用于帮助模型更准确地理解如何使用该参数。例如:参数格式要求、允许取值范围等。 -
required:指定参数是否为必需项(默认值:true,即所有参数默认必需)。
若参数标注了 @Nullable 注解,则该参数将被视为可选参数,除非通过 @ToolParam 显式标记为必需参数
除 @ToolParam 注解外,你还可使用 Swagger 的 @Schema 或 Jackson 的 @JsonProperty 注解。详见 JSON Schema 章节说明。
为 ChatClient 添加工具
当使用声明式配置方案时,你可以在调用 ChatClient 时通过 tools() 方法传入工具类实例。此类工具仅在添加它们的特定聊天请求中可用。
ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What day is tomorrow?")
.tools(new DateTimeTools())
.call()
.content();在底层实现中,ChatClient 会从工具类实例的每个 @Tool 注解方法生成对应的 ToolCallback,并将其传递给模型。若你希望自行生成 ToolCallback,可使用 ToolCallbacks 工具类。
ToolCallback[] dateTimeTools = ToolCallbacks.from(new DateTimeTools());为 ChatClient 添加默认工具
当使用声明式配置方案时,你可以通过向 ChatClient.Builder 的 defaultTools() 方法传入工具类实例来添加默认工具。若同时提供默认工具和运行时工具,运行时工具将完全覆盖默认工具。
默认工具在所有基于同一 ChatClient.Builder 构建的 ChatClient 实例执行的聊天请求间共享。此类工具适用于跨聊天请求的通用功能,但若使用不当可能存在风险 — 导致工具在不该出现的场景中可用。
|
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultTools(new DateTimeTools())
.build();为 ChatModel 添加工具
当使用声明式配置方案时,你可以通过调用 ChatModel 时使用的 ToolCallingChatOptions 中的 toolCallbacks() 方法传入工具类实例。此类工具仅在添加它们的特定聊天请求中可用。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallback[] dateTimeTools = ToolCallbacks.from(new DateTimeTools());
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(dateTimeTools)
.build();
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("What day is tomorrow?", chatOptions);
chatModel.call(prompt);为 ChatModel 添加默认工具
当使用声明式配置方案时,你可以在构建 ChatModel 时通过 ToolCallingChatOptions 实例的 toolCallbacks() 方法传入工具类实例来添加默认工具。若同时提供默认工具和运行时工具,运行时工具将完全覆盖默认工具。
默认工具在该 ChatModel 实例执行的所有聊天请求间共享。此类工具适用于跨请求的通用功能,但需谨慎使用 — 否则可能导致工具在不该被调用的场景下可用。
|
ToolCallback[] dateTimeTools = ToolCallbacks.from(new DateTimeTools());
ChatModel chatModel = OllamaChatModel.builder()
.ollamaApi(OllamaApi.builder().build())
.defaultOptions(ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(dateTimeTools)
.build())
.build();编程式配置:MethodToolCallback 方案
你可以通过编程式构建 MethodToolCallback 来将方法转换为工具。
class DateTimeTools {
String getCurrentDateTime() {
return LocalDateTime.now().atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId()).toString();
}
}MethodToolCallback.Builder 允许你构建 MethodToolCallback 实例并配置以下关键工具信息:
-
toolDefinition:定义工具名称、描述及输入模式的ToolDefinition实例(必需项),可通过ToolDefinition.Builder类构建。 -
toolMetadata:定义额外设置的ToolMetadata实例(如是否将结果直接返回客户端、使用的结果转换器等),可通过ToolMetadata.Builder类构建。 -
toolMethod:表示工具方法的Method实例(必需项)。 -
toolObject:包含工具方法的对象实例(若方法为静态方法则可省略此参数)。 -
toolCallResultConverter:用于将工具调用结果转换为 String 对象并返回 AI 模型的ToolCallResultConverter实例(未配置时默认使用DefaultToolCallResultConverter)。
ToolDefinition.Builder 允许你构建 ToolDefinition 实例并定义以下工具属性:
-
name:工具名称。若未指定,默认使用方法名称。AI 模型通过此名称识别调用工具,因此不允许在同一类中存在同名工具。模型处理单个聊天请求时,所有可用工具的名称必须保持全局唯一。 -
description:工具描述,用于帮助模型理解何时及如何调用该工具。若未提供,将使用方法名称作为工具描述。但强烈建议提供详细描述,因为这对模型理解工具的用途及使用方法至关重要。若描述不充分,可能导致模型在该调用工具时未调用,或错误调用工具。 -
inputSchema:工具输入参数的 JSON 模式。若未提供,将根据方法参数自动生成模式。你可使用@ToolParam注解提供输入参数的额外信息(如描述、是否必需等),默认情况下所有输入参数均为必需参数。详见 JSON Schema 章节说明。
ToolMetadata.Builder 允许你构建 ToolMetadata 实例并为工具定义以下附加设置:
-
returnDirect:控制是否将工具结果直接返回客户端(true)还是传回模型(false)。详见 [_return_direct] 章节说明。
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "getCurrentDateTime");
ToolCallback toolCallback = MethodToolCallback.builder()
.toolDefinition(ToolDefinition.builder(method)
.description("Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
.build())
.toolMethod(method)
.toolObject(new DateTimeTools())
.build();该方法既可以是静态方法也可以是实例方法,并且可具有任意可见性(public、protected、package-private 或 private)。包含该方法的类既可以是顶级类也可以是嵌套类,同样支持任意可见性(只要在计划实例化的位置可访问即可)。
Spring AI 为工具方法提供内置的 AOT(提前编译)支持,前提是包含这些方法的类必须是 Spring Bean(例如使用 @Component 注解)。否则,你需要为 GraalVM 编译器提供必要的配置,例如通过使用 @RegisterReflection(memberCategories = MemberCategory.INVOKE_DECLARED_METHODS) 注解标记该类。
|
你可以为方法定义任意数量的参数(包括无参数),支持大多数类型(基本类型、POJO、枚举、List、数组、Map 等)。同样,方法可以返回大多数类型,包括 void。若方法有返回值,则返回类型必须是可序列化类型,因为结果将被序列化并发送回模型。
| 部分类型不受支持。详见方法工具限制([_method_tool_limitations])章节说明。 |
若方法为静态方法,则可省略 toolObject() 方法(因其非必需)。
class DateTimeTools {
static String getCurrentDateTime() {
return LocalDateTime.now().atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId()).toString();
}
}Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "getCurrentDateTime");
ToolCallback toolCallback = MethodToolCallback.builder()
.toolDefinition(ToolDefinition.builder(method)
.description("Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
.build())
.toolMethod(method)
.build();Spring AI 将自动生成方法输入参数的 JSON 模式。该模式供模型理解如何调用工具及准备工具请求。你可使用 @ToolParam 注解为输入参数提供额外信息(如描述、是否必需等),默认情况下所有输入参数均为必需参数。
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.ToolParam;
class DateTimeTools {
void setAlarm(@ToolParam(description = "Time in ISO-8601 format") String time) {
LocalDateTime alarmTime = LocalDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
System.out.println("Alarm set for " + alarmTime);
}
}@ToolParam 注解允许你配置工具参数的以下关键信息:
-
description:参数描述,用于帮助模型更准确地理解如何使用该参数。例如:参数格式要求、允许取值范围等。 -
required:指定参数是否为必需项(默认值:true,即所有参数默认必需)。
若参数标注了 @Nullable 注解,则该参数将被视为可选参数,除非通过 @ToolParam 显式标记为必需参数。
除 @ToolParam 注解外,你还可使用 Swagger 的 @Schema 或 Jackson 的 @JsonProperty 注解。详见 JSON Schema 章节说明。
为 ChatClient 与 ChatModel 添加工具
当使用编程式配置方案时,你可以通过 ChatClient 的 tools() 方法传入 MethodToolCallback 实例。该工具仅在添加它的特定聊天请求中可用。
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What day is tomorrow?")
.tools(toolCallback)
.call()
.content();为 ChatClient 添加默认工具
当使用编程式配置方案时,你可以通过向 ChatClient.Builder 的 defaultTools() 方法传入 MethodToolCallback 实例来添加默认工具。若同时提供默认工具和运行时工具,运行时工具将完全覆盖默认工具。
默认工具在所有基于同一 ChatClient.Builder 构建的 ChatClient 实例执行的聊天请求间共享。此类工具适用于跨聊天请求的通用功能,但若使用不当可能存在风险 — 导致工具在不该出现的场景中可用。
|
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultTools(toolCallback)
.build();为 ChatModel 添加工具
当使用编程式配置方案时,你可以通过调用 ChatModel 时使用的 ToolCallingChatOptions 中的 toolCallbacks() 方法传入 MethodToolCallback 实例。该工具仅在添加它的特定聊天请求中可用。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.build():
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("What day is tomorrow?", chatOptions);
chatModel.call(prompt);为 ChatModel 添加默认工具
使用编程式配置方案时,你可以在构建 ChatModel 时,通过用于创建 ChatModel 的 ToolCallingChatOptions 实例的 toolCallbacks() 方法传入 MethodToolCallback 实例来添加默认工具。若同时提供默认工具和运行时工具,运行时工具将完全覆盖默认工具。
默认工具在该 ChatModel 实例处理的所有聊天请求间共享。此类工具适用于跨聊天请求的通用功能,但若使用不当,可能导致工具在不该出现的场景中被调用。
|
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatModel chatModel = OllamaChatModel.builder()
.ollamaApi(OllamaApi.builder().build())
.defaultOptions(ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.build())
.build();方法工具的限制
以下类型目前不支持作为工具方法的参数或返回类型:
-
Optional -
异步类型(如
CompletableFuture、Future) -
响应式类型 (如
Flow、Mono、Flux) -
函数式类型(如
Function、Supplier、Consumer)
函数式类型在基于函数的工具规范方法中受支持。详见 “[_functions_as_tools]” 章节说明。
函数即工具
Spring AI 内置支持通过函数定义工具,既可通过底层的 FunctionToolCallback 实现以编程方式配置,也能作为运行时解析的 @Bean 动态注册。
编程式规范:FunctionToolCallback
你可以通过编程方式构建 FunctionToolCallback,将函数式类型(Function、Supplier、Consumer 或 BiFunction)转换为工具。
public class WeatherService implements Function<WeatherRequest, WeatherResponse> {
public WeatherResponse apply(WeatherRequest request) {
return new WeatherResponse(30.0, Unit.C);
}
}
public enum Unit { C, F }
public record WeatherRequest(String location, Unit unit) {}
public record WeatherResponse(double temp, Unit unit) {}FunctionToolCallback.Builder 允许你构建 FunctionToolCallback 实例并提供以下关键工具信息:
-
name:工具名称。AI 模型通过此名称识别调用工具,因此同一上下文中不允许存在同名工具。对于特定聊天请求,模型可用的所有工具名称必须保持全局唯一。(必需项) -
toolFunction:表示工具方法的函数式对象(Function、Supplier、Consumer或BiFunction)。(必需项) -
description:工具描述,用于帮助模型判断何时及如何调用该工具。若未提供,将使用方法名称作为工具描述。但强烈建议提供详细描述,这对模型理解工具用途及使用方法至关重要。若描述不充分,可能导致模型在该调用工具时未调用,或错误调用工具。 -
inputType:函数输入类型。(必需项) -
inputSchema:工具输入参数的 JSON Schema。若未提供,将基于inputType自动生成 Schema。你可使用@ToolParam注解提供输入参数的额外信息(如描述、是否必需等),默认情况下所有输入参数均为必需参数。详见 JSON Schema 章节说明。 -
toolMetadata:定义额外设置的ToolMetadata实例(如是否将结果直接返回客户端、使用的结果转换器等),可通过ToolMetadata.Builder类构建。 -
toolCallResultConverter:用于将工具调用结果转换为String对象并返回 AI 模型的ToolCallResultConverter实例(未配置时默认使用DefaultToolCallResultConverter)。
ToolMetadata.Builder 允许你构建 ToolMetadata 实例并为工具定义以下附加设置:
-
returnDirect:控制工具结果直接返回客户端(true)还是传回模型(false)。详见 [_return_direct] 章节说明。
ToolCallback toolCallback = FunctionToolCallback
.builder("currentWeather", new WeatherService())
.description("Get the weather in location")
.inputType(WeatherRequest.class)
.build();函数输入和输出可以是 Void 或 POJO。输入和输出的 POJO 必须是可序列化的,因为结果将被序列化并发送回模型。函数及输入输出类型必须是 public 的。
| 部分类型不受支持。详见 “[_function_tool_limitations]” 章节说明。 |
为 ChatClient 添加工具
使用编程式规范时,你可以将 FunctionToolCallback 实例传递给 ChatClient 的 tools() 方法。该工具仅在添加它的特定聊天请求中可用。
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What's the weather like in Copenhagen?")
.tools(toolCallback)
.call()
.content();为 ChatClient 添加默认工具
使用编程式规范时,你可以通过将 FunctionToolCallback 实例传递给 ChatClient.Builder 的 defaultTools() 方法来添加默认工具。若同时提供默认工具和运行时工具,运行时工具将完全覆盖默认工具。
默认工具在所有基于同一 ChatClient.Builder 构建的 ChatClient 实例执行的聊天请求间共享。此类工具适用于跨聊天请求的通用功能,但若使用不当,可能导致工具在不该出现的场景中被调用。
|
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultTools(toolCallback)
.build();为 ChatModel 添加工具
使用编程式规范时,你可以将 FunctionToolCallback 实例传递给 ToolCallingChatOptions 的 toolCallbacks() 方法。该工具仅在添加它的特定聊天请求中可用。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.build():
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("What's the weather like in Copenhagen?", chatOptions);
chatModel.call(prompt);为 ChatModel 添加默认工具
使用编程式规范时,你可以在构建 ChatModel 时,通过用于创建 ChatModel 的 ToolCallingChatOptions 实例的 toolCallbacks() 方法传入 FunctionToolCallback 实例来添加默认工具。若同时提供默认工具和运行时工具,运行时工具将完全覆盖默认工具。
默认工具在该 ChatModel 实例处理的所有聊天请求间共享。此类工具适用于跨聊天请求的通用功能,但若使用不当,可能导致工具在不该出现的场景中被调用。
|
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatModel chatModel = OllamaChatModel.builder()
.ollamaApi(OllamaApi.builder().build())
.defaultOptions(ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.build())
.build();动态规范:@Bean
无需编程式配置工具,你可将工具定义为 Spring Bean,由 Spring AI 通过 ToolCallbackResolver 接口(具体实现为 SpringBeanToolCallbackResolver)在运行时动态解析。此方案支持将任意 Function、Supplier、Consumer 或 BiFunction 类型的 Bean 作为工具使用。Bean 名称将作为工具名称,可通过 Spring Framework 的 @Description 注解提供工具描述(用于指导模型判断调用时机及方式)。若未提供描述,则使用方法名称作为工具描述。但强烈建议提供详细描述,这对模型理解工具用途及使用方法至关重要。若描述不充分,可能导致模型在该调用工具时未调用,或错误调用工具。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
class WeatherTools {
WeatherService weatherService = new WeatherService();
@Bean
@Description("Get the weather in location")
Function<WeatherRequest, WeatherResponse> currentWeather() {
return weatherService;
}
}| 部分类型不受支持。详见 “[_function_tool_limitations]” 章节说明。 |
工具输入参数的 JSON Schema 将自动生成。你可使用 @ToolParam 注解提供输入参数的额外信息(如描述、是否必需等),默认情况下所有输入参数均为必需参数。详见 JSON Schema 章节说明。
record WeatherRequest(@ToolParam(description = "The name of a city or a country") String location, Unit unit) {}该工具规范方案存在无法保证类型安全的缺点(因工具解析在运行时完成)。要解决此问题,你可通过 @Bean 注解显式指定工具名称,并将名称存储在常量中,以便在聊天请求中使用该常量而非硬编码工具名称。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
class WeatherTools {
public static final String CURRENT_WEATHER_TOOL = "currentWeather";
@Bean(CURRENT_WEATHER_TOOL)
@Description("Get the weather in location")
Function<WeatherRequest, WeatherResponse> currentWeather() {
...
}
}为 ChatClient 添加工具
使用动态规范方式时,你可以将工具名称(即函数 bean 名称)传递给 ChatClient 的 tools() 方法。该工具仅在添加它的特定聊天请求中可用。
ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What's the weather like in Copenhagen?")
.tools("currentWeather")
.call()
.content();为 ChatClient 添加默认工具
使用动态规范方式时,你可以通过将工具名称传递给 ChatClient.Builder 的 defaultTools() 方法来添加默认工具。若同时提供默认工具和运行时工具,运行时工具将完全覆盖默认工具。
默认工具在所有基于同一 ChatClient.Builder 构建的 ChatClient 实例执行的聊天请求间共享。此类工具适用于跨聊天请求的通用功能,但若使用不当,可能导致工具在不该出现的场景中被调用。
|
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultTools("currentWeather")
.build();为 ChatModel 添加工具
使用动态规范方式时,你可以通过调用 ChatModel 时使用的 ToolCallingChatOptions 中的 toolNames() 方法传入工具名称。该工具仅在添加它的特定聊天请求中可用。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolNames("currentWeather")
.build():
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("What's the weather like in Copenhagen?", chatOptions);
chatModel.call(prompt);为 ChatModel 添加默认工具
使用动态规范方式时,你可以在构建 ChatModel 时,通过用于创建 ChatModel 的 ToolCallingChatOptions 实例的 toolNames() 方法传入工具名称来添加默认工具。若同时提供默认工具和运行时工具,运行时工具将完全覆盖默认工具。
默认工具在该 ChatModel 实例处理的所有聊天请求间共享。此类工具适用于跨聊天请求的通用功能,但若使用不当,可能导致工具在不该出现的场景中被调用。
|
ChatModel chatModel = OllamaChatModel.builder()
.ollamaApi(OllamaApi.builder().build())
.defaultOptions(ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolNames("currentWeather")
.build())
.build();函数式工具的限制
以下类型目前不支持作为工具函数的输入或输出类型:
-
基本类型
-
Optional -
集合类型 (如
List、Map、Array、Set) -
异步类型(如
CompletableFuture、Future) -
响应式类型(如
Flow、Mono、Flux)
基本类型和集合在使用基于方法的工具规范方案时受支持。详见 “[_methods_as_tools]” 章节说明。
工具规范
在 Spring AI 中,工具通过 ToolCallback 接口建模。前文我们已了解如何利用 Spring AI 内置支持从方法和函数定义工具(参见 “[_methods_as_tools]” 和 “[_functions_as_tools]” 章节)。本节将深入探讨工具规范,以及如何定制扩展以支持更多用例。
ToolCallback
ToolCallback 接口提供了定义 AI 模型可调用工具的方式,包含工具定义和执行逻辑。当需要从头定义工具时,这是需实现的主要接口。例如:你可以从 MCP 客户端(使用模型上下文协议)或 ChatClient(用于构建模块化代理应用)创建 ToolCallback 实例。
该接口提供以下方法:
public interface ToolCallback {
/**
* Definition used by the AI model to determine when and how to call the tool.
*/
ToolDefinition getToolDefinition();
/**
* Metadata providing additional information on how to handle the tool.
*/
ToolMetadata getToolMetadata();
/**
* Execute tool with the given input and return the result to send back to the AI model.
*/
String call(String toolInput);
/**
* Execute tool with the given input and context, and return the result to send back to the AI model.
*/
String call(String toolInput, ToolContext tooContext);
}Spring AI 为工具方法(MethodToolCallback)和工具函数(FunctionToolCallback)提供了内置实现。
ToolDefinition
ToolDefinition 接口提供 AI 模型识别工具可用性所需的信息,包括工具名称、描述及输入模式。每个 ToolCallback 实现必须提供 ToolDefinition 实例来定义工具。
接口定义如下:
public interface ToolDefinition {
/**
* The tool name. Unique within the tool set provided to a model.
*/
String name();
/**
* The tool description, used by the AI model to determine what the tool does.
*/
String description();
/**
* The schema of the parameters used to call the tool.
*/
String inputSchema();
}| 详见 JSON Schema 章节获取输入模式的更多细节。 |
ToolDefinition.Builder 允许你使用默认实现(DefaultToolDefinition)构建 ToolDefinition 实例。
ToolDefinition toolDefinition = ToolDefinition.builder()
.name("currentWeather")
.description("Get the weather in location")
.inputSchema("""
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["C", "F"]
}
},
"required": ["location", "unit"]
}
""")
.build();方法工具定义
基于方法构建工具时,ToolDefinition 会自动生成。若需自行创建,可使用此便捷 Builder。
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "getCurrentDateTime");
ToolDefinition toolDefinition = ToolDefinition.from(method);从方法生成的 ToolDefinition 包含:方法名作为工具名称、方法名作为工具描述,以及方法输入参数的 JSON Schema。若方法使用 @Tool 注解,则工具名称和描述将优先采用注解中的设定值(若已设置)。
| 详见 “[_methods_as_tools]” 章节获取更多细节。 |
若需显式指定部分或全部属性,可使用 ToolDefinition.Builder 构建自定义的 ToolDefinition 实例。
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "getCurrentDateTime");
ToolDefinition toolDefinition = ToolDefinition.builder(method)
.name("currentDateTime")
.description("Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
.inputSchema(JsonSchemaGenerator.generateForMethodInput(method))
.build();函数工具定义
基于函数构建工具时,ToolDefinition 会自动生成。使用 FunctionToolCallback.Builder 构建 FunctionToolCallback 实例时,可指定用于生成 ToolDefinition 的工具名称、描述及输入模式。详见 “[_functions_as_tools]” 章节。
JSON Schema
向 AI 模型提供工具时,模型需要知道工具调用输入类型的模式。该模式用于理解如何调用工具及准备工具请求。Spring AI 通过 JsonSchemaGenerator 类内置支持生成工具输入类型的 JSON Schema,该模式作为 ToolDefinition 的一部分提供。
| 详见 “[_tool_definition]” 章节获取关于ToolDefinition及如何传递输入模式的更多细节。 |
JsonSchemaGenerator 类在底层用于生成方法或函数输入参数的 JSON Schema,支持 “[_methods_as_tools]” 和 “[_functions_as_tools]” 章节描述的所有策略。其模式生成逻辑支持一系列注解,你可在方法/函数的输入参数上使用这些注解来自定义生成的 Schema。
本节描述生成工具输入参数 JSON Schema 时可定制的两个主要选项:描述信息(description)和必需状态(required)。
描述
除了为工具本身提供描述外,你还可为工具的输入参数添加描述。该描述可用于提供参数的关键信息,如参数格式要求、允许取值等,有助于模型理解输入模式及使用方法。Spring AI 内置支持通过以下注解生成输入参数描述:
-
Spring AI 的
@ToolParam(description = "…") -
Jackson 的
@JsonClassDescription(description = "…") -
Jackson 的
@JsonPropertyDescription(description = "…") -
Swagger 的
@Schema(description = "…")
此方案同时适用于方法和函数,且可递归应用于嵌套类型。
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.Tool;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.ToolParam;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
class DateTimeTools {
@Tool(description = "Set a user alarm for the given time")
void setAlarm(@ToolParam(description = "Time in ISO-8601 format") String time) {
LocalDateTime alarmTime = LocalDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
System.out.println("Alarm set for " + alarmTime);
}
}必须/可选
默认情况下,每个输入参数都被视为必需参数,这会强制 AI 模型在调用工具时必须提供该参数值。但你可通过以下注解(按优先级顺序)将输入参数设为可选:
-
Spring AI 的
@ToolParam(required = false) -
Jackson 的
@JsonProperty(required = false) -
Swagger 的
@Schema(required = false) -
Spring 的
@Nullable
此方法同时适用于方法和函数,并可递归应用于嵌套类型。
class CustomerTools {
@Tool(description = "Update customer information")
void updateCustomerInfo(Long id, String name, @ToolParam(required = false) String email) {
System.out.println("Updated info for customer with id: " + id);
}
}
正确定义输入参数的必需状态对降低幻觉风险至关重要,能确保模型调用工具时提供正确的输入。在前例中,email 参数为可选,意味着模型可不提供该参数值直接调用工具。若参数为必需,则模型调用时必须提供参数值 — 当不存在有效值时,模型可能会虚构参数值,从而导致幻觉。
|
结果转换
工具调用结果通过 ToolCallResultConverter 序列化后返回 AI 模型。该接口提供将工具调用结果转换为 String 对象的能力。
接口定义如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ToolCallResultConverter {
/**
* Given an Object returned by a tool, convert it to a String compatible with the
* given class type.
*/
String convert(@Nullable Object result, @Nullable Type returnType);
}结果必须是可序列化类型。默认情况下,结果通过 Jackson 序列化为 JSON(使用 DefaultToolCallResultConverter),但你可通过自定义 ToolCallResultConverter 实现来定制序列化过程。
Spring AI 在方法和函数工具中均依赖 ToolCallResultConverter。
方法工具调用结果转换
使用声明式方法从方法构建工具时,你可以通过设置 @Tool 注解的 resultConverter() 属性来为该工具提供自定义的 ToolCallResultConverter。
class CustomerTools {
@Tool(description = "Retrieve customer information", resultConverter = CustomToolCallResultConverter.class)
Customer getCustomerInfo(Long id) {
return customerRepository.findById(id);
}
}若使用编程式方法,可通过设置 MethodToolCallback.Builder 的 resultConverter() 属性来为工具提供自定义的 ToolCallResultConverter。
详见 “[_methods_as_tools]” 章节获取更多细节。
函数工具调用结果转换
使用编程式方法从函数构建工具时,你可以通过设置 FunctionToolCallback.Builder 的 resultConverter() 属性来为该工具提供自定义的 ToolCallResultConverter。
详见 “[_functions_as_tools]” 章节获取更多细节。
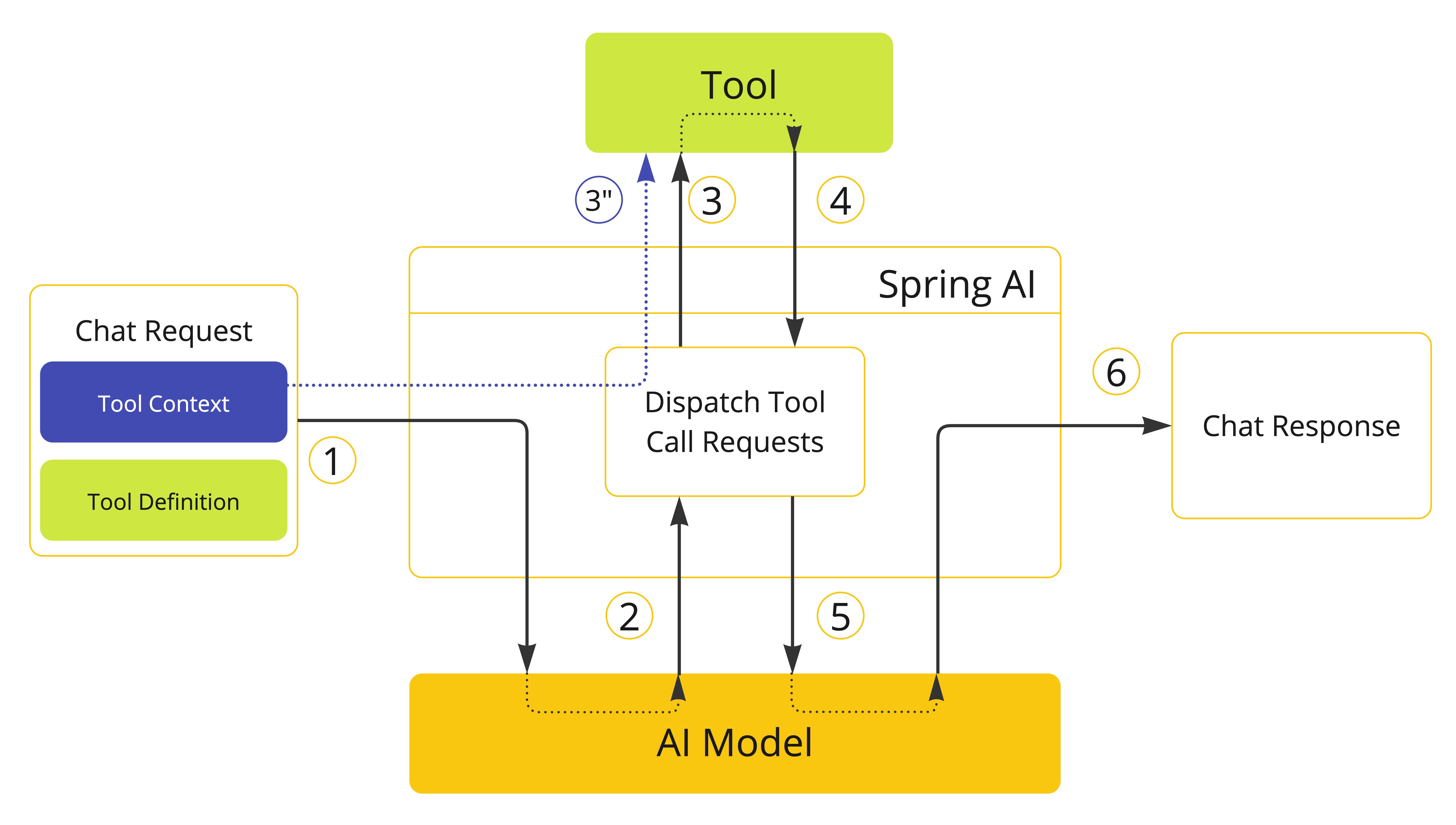
ToolContext
Spring AI 支持通过 ToolContext API 向工具传递额外的上下文信息。此功能允许你提供用户自定义的额外数据,这些数据可与 AI 模型传递的工具参数一起在工具执行过程中使用。
class CustomerTools {
@Tool(description = "Retrieve customer information")
Customer getCustomerInfo(Long id, ToolContext toolContext) {
return customerRepository.findById(id, toolContext.get("tenantId"));
}
}ToolContext 中的数据由用户调用 ChatClient 时提供。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("Tell me more about the customer with ID 42")
.tools(new CustomerTools())
.toolContext(Map.of("tenantId", "acme"))
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(response);
ToolContext 中提供的任何数据都不会发送给 AI 模型。
|
同样,直接调用 ChatModel 时也可定义工具上下文数据。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallback[] customerTools = ToolCallbacks.from(new CustomerTools());
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(customerTools)
.toolContext(Map.of("tenantId", "acme"))
.build();
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("Tell me more about the customer with ID 42", chatOptions);
chatModel.call(prompt);若在默认选项和运行时选项中均设置了 toolContext,最终 ToolContext 将是两者的合并结果,其中运行时选项优先于默认选项。
直接返回
默认情况下,工具调用结果将作为响应返回模型,随后模型可利用该结果继续对话。
某些场景下,你可能希望将结果直接返回调用方而非传回模型。例如:当构建依赖 RAG 工具的代理时,你可能希望直接将检索结果返回调用方,而非传回模型进行不必要的后处理;又或者某些工具应当终止代理的推理循环。
每个 ToolCallback 实现均可定义工具调用结果应直接返回调用方还是传回模型。默认结果为传回模型,但你可按工具单独修改此行为。
ToolCallingManager 负责管理工具执行生命周期,其会处理工具的 returnDirect 属性。若该属性设为 true,工具调用结果将直接返回调用方;否则结果将传回模型。
若同时请求多个工具调用,则所有工具的 returnDirect 属性必须设为 true 才能将结果直接返回调用方。否则,结果将传回模型。
|
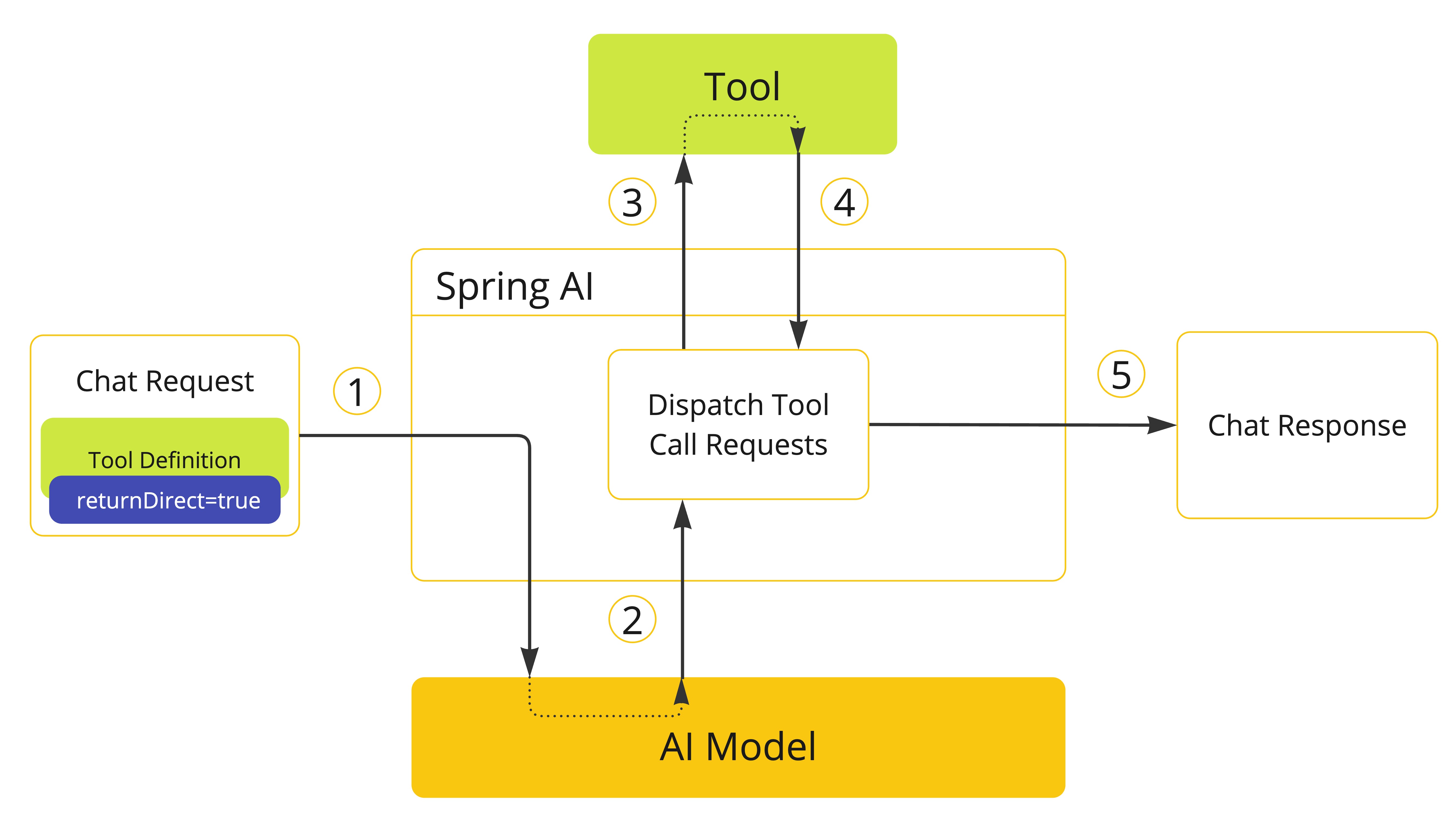
-
当需要向模型提供工具时,我们将其定义包含在聊天请求中。若希望工具执行结果直接返回调用方,则将
returnDirect属性设为true。 -
当模型决定调用工具时,它会发送一个响应,其中包含工具名称和根据定义的模式建模的输入参数。
-
应用程序负责使用工具名称来识别并使用提供的输入参数执行工具。
-
工具调用的结果由应用程序处理。
-
应用程序将工具调用结果直接返回调用方,而非传回模型。
方法直接返回
使用声明式方法从方法构建工具时,你可以通过将 @Tool 注解的 returnDirect 属性设为 true,将工具标记为直接向调用方返回结果。
class CustomerTools {
@Tool(description = "Retrieve customer information", returnDirect = true)
Customer getCustomerInfo(Long id) {
return customerRepository.findById(id);
}
}若使用编程式方法,可通过 ToolMetadata 接口设置 returnDirect 属性,并将其传递给 MethodToolCallback.Builder。
ToolMetadata toolMetadata = ToolMetadata.builder()
.returnDirect(true)
.build();查看 “[_methods_as_tools]” 了解更多详情。
函数直接返回
使用编程式方法从函数构建工具时,你可通过 ToolMetadata 接口设置 returnDirect 属性,并将其传递给 FunctionToolCallback.Builder。
ToolMetadata toolMetadata = ToolMetadata.builder()
.returnDirect(true)
.build();详见 “[_functions_as_tools]” 章节获取更多细节。
工具执行
工具执行是指使用提供的输入参数调用工具并返回结果的过程。该过程由 ToolCallingManager 接口处理,该接口负责管理工具执行的完整生命周期。
public interface ToolCallingManager {
/**
* Resolve the tool definitions from the model's tool calling options.
*/
List<ToolDefinition> resolveToolDefinitions(ToolCallingChatOptions chatOptions);
/**
* Execute the tool calls requested by the model.
*/
ToolExecutionResult executeToolCalls(Prompt prompt, ChatResponse chatResponse);
}若使用 Spring AI Spring Boot Starter,DefaultToolCallingManager 将作为 ToolCallingManager 接口的自动配置实现。你可通过提供自定义的 ToolCallingManager Bean 来定制工具执行行为。
@Bean
ToolCallingManager toolCallingManager() {
return ToolCallingManager.builder().build();
}默认情况下,Spring AI 在每个 ChatModel 实现中透明地管理工具执行生命周期。但你可选择退出此行为,自行控制工具执行。本节将描述这两种场景。
框架控制的工具执行
使用默认行为时,Spring AI 会自动拦截模型的工具调用请求,执行工具并将结果返回模型。这些操作均由各 ChatModel 实现通过 ToolCallingManager 透明完成。
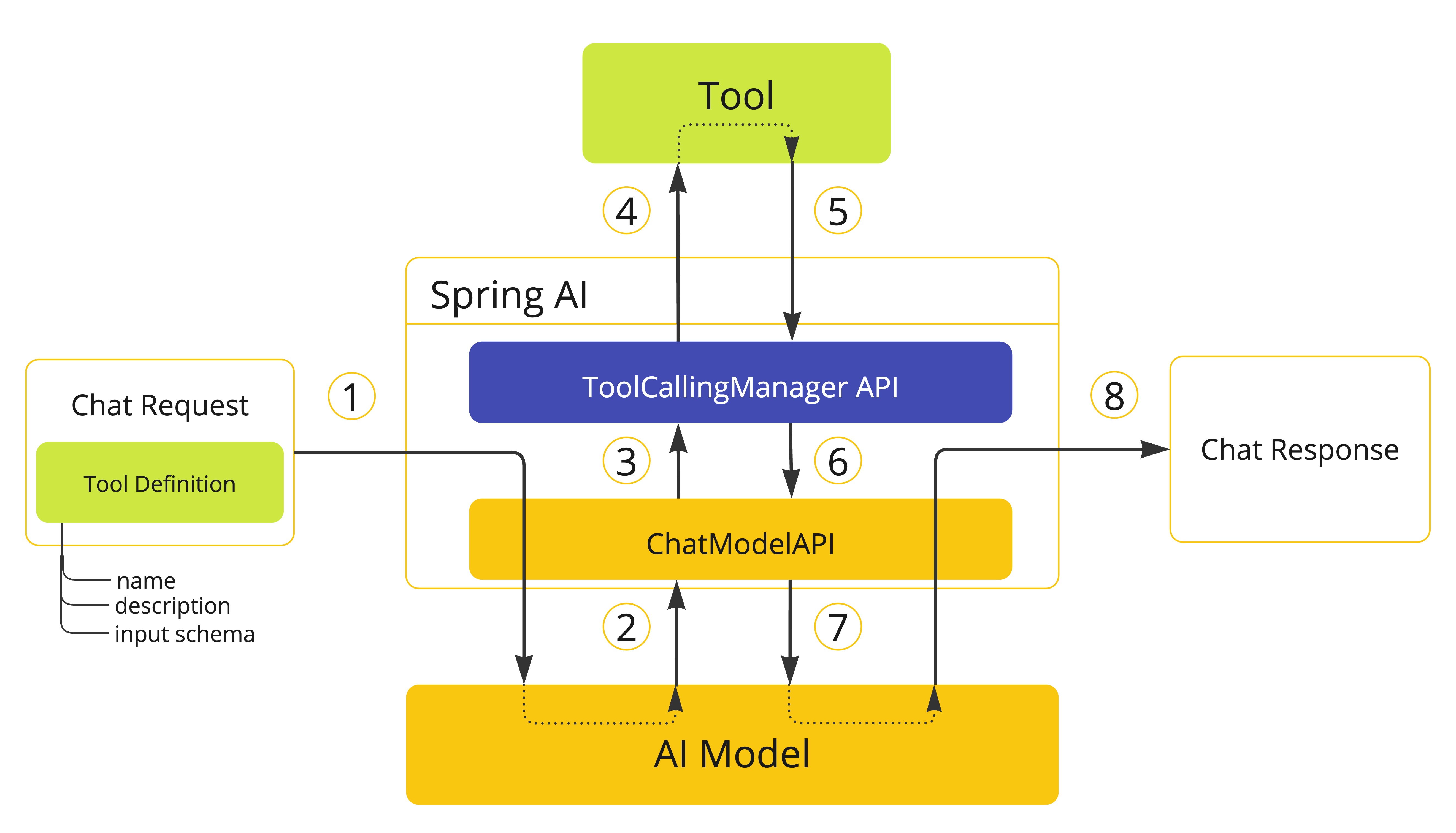
-
当需要向模型提供工具时,我们将其定义包含在聊天请求(
Prompt)中,并调用ChatModelAPI 将请求发送至 AI 模型。 -
当模型决定调用工具时,它会发送包含工具名称及符合定义模式的输入参数的响应(
ChatResponse)。 -
ChatModel将工具调用请求发送至ToolCallingManagerAPI。 -
ToolCallingManager负责识别需调用的工具并使用提供的输入参数执行该工具。 -
工具调用结果返回至
ToolCallingManager。 -
ToolCallingManager将工具执行结果返回给ChatModel。 -
ChatModel将工具执行结果返回AI模型(ToolResponseMessage)。 -
AI 模型利用工具调用结果作为附加上下文生成最终响应,并通过
ChatClient将其返回调用方(ChatResponse)。
| 目前与模型交互的工具执行内部消息未向用户公开。如需访问这些消息,应采用用户控制的工具执行方案。 |
工具调用是否具备执行资格的逻辑由 ToolExecutionEligibilityPredicate 接口处理。默认情况下,通过检查 ToolCallingChatOptions 的 internalToolExecutionEnabled 属性(默认值为 true)及 ChatResponse 是否包含工具调用来判定执行资格。
public class DefaultToolExecutionEligibilityPredicate implements ToolExecutionEligibilityPredicate {
@Override
public boolean test(ChatOptions promptOptions, ChatResponse chatResponse) {
return ToolCallingChatOptions.isInternalToolExecutionEnabled(promptOptions) && chatResponse != null
&& chatResponse.hasToolCalls();
}
}创建 ChatModel Bean 时,你可提供自定义的 ToolExecutionEligibilityPredicate 实现。
用户控制的工具执行
某些情况下,你可能希望自行控制工具执行生命周期。此时可将 ToolCallingChatOptions 的 internalToolExecutionEnabled 属性设为 false。
当使用此选项调用 ChatModel 时,工具执行将委托给调用方,由你完全控制工具执行生命周期。你需要检查 ChatResponse 中的工具调用,并使用 ToolCallingManager 执行它们。
以下示例演示了用户控制工具执行方案的最小实现:
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallingManager toolCallingManager = ToolCallingManager.builder().build();
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(new CustomerTools())
.internalToolExecutionEnabled(false)
.build();
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("Tell me more about the customer with ID 42", chatOptions);
ChatResponse chatResponse = chatModel.call(prompt);
while (chatResponse.hasToolCalls()) {
ToolExecutionResult toolExecutionResult = toolCallingManager.executeToolCalls(prompt, chatResponse);
prompt = new Prompt(toolExecutionResult.conversationHistory(), chatOptions);
chatResponse = chatModel.call(prompt);
}
System.out.println(chatResponse.getResult().getOutput().getText());
选择用户控制的工具执行方案时,建议使用 ToolCallingManager 管理工具调用操作。这样可充分利用 Spring AI 内置的工具执行支持。当然,你也可完全自行实现工具执行逻辑。
|
下面的示例展示了结合使用 ChatMemory API 的用户控制工具执行方案的最小实现:
ToolCallingManager toolCallingManager = DefaultToolCallingManager.builder().build();
ChatMemory chatMemory = MessageWindowChatMemory.builder().build();
String conversationId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(ToolCallbacks.from(new MathTools()))
.internalToolExecutionEnabled(false)
.build();
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(
List.of(new SystemMessage("You are a helpful assistant."), new UserMessage("What is 6 * 8?")),
chatOptions);
chatMemory.add(conversationId, prompt.getInstructions());
Prompt promptWithMemory = new Prompt(chatMemory.get(conversationId), chatOptions);
ChatResponse chatResponse = chatModel.call(promptWithMemory);
chatMemory.add(conversationId, chatResponse.getResult().getOutput());
while (chatResponse.hasToolCalls()) {
ToolExecutionResult toolExecutionResult = toolCallingManager.executeToolCalls(promptWithMemory,
chatResponse);
chatMemory.add(conversationId, toolExecutionResult.conversationHistory()
.get(toolExecutionResult.conversationHistory().size() - 1));
promptWithMemory = new Prompt(chatMemory.get(conversationId), chatOptions);
chatResponse = chatModel.call(promptWithMemory);
chatMemory.add(conversationId, chatResponse.getResult().getOutput());
}
UserMessage newUserMessage = new UserMessage("What did I ask you earlier?");
chatMemory.add(conversationId, newUserMessage);
ChatResponse newResponse = chatModel.call(new Prompt(chatMemory.get(conversationId)));异常处理
当工具调用失败时,异常会以 ToolExecutionException 形式传播,可捕获该异常进行错误处理。通过 ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor 可处理 ToolExecutionException,产生两种结果:生成返回 AI 模型的错误信息,或抛出由调用方处理的异常。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor {
/**
* Convert an exception thrown by a tool to a String that can be sent back to the AI
* model or throw an exception to be handled by the caller.
*/
String process(ToolExecutionException exception);
}若使用 Spring AI Spring Boot Starter,DefaultToolExecutionExceptionProcessor 将作为 ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor 接口的自动配置实现。默认会将错误信息返回模型。通过 DefaultToolExecutionExceptionProcessor 构造函数的 alwaysThrow 参数(设为 true 时抛出异常而非返回错误信息)可修改此行为。
你可通过 spring.ai.tools.throw-exception-on-error 属性控制 DefaultToolExecutionExceptionProcessor Bean 的行为:
| 属性 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
|
若为 |
|
@Bean
ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor toolExecutionExceptionProcessor() {
return new DefaultToolExecutionExceptionProcessor(true);
}
若自定义 ToolCallback 实现,请确保在 call() 方法的工具执行逻辑中发生错误时抛出 ToolExecutionException。
|
ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor 由默认的 ToolCallingManager(DefaultToolCallingManager)内部使用,用于处理工具执行期间的异常。有关工具执行生命周期的更多详情,请参阅 “[_tool_execution]” 章节。
工具解析
向模型传递工具的主要方法是在调用 ChatClient 或 ChatModel 时提供 ToolCallback 实例,采用 “[_methods_as_tools]” 和 “[_functions_as_tools]” 章节所述的策略之一。
然而,Spring AI 还支持通过 ToolCallbackResolver 接口在运行时动态解析工具。
public interface ToolCallbackResolver {
/**
* Resolve the {@link ToolCallback} for the given tool name.
*/
@Nullable
ToolCallback resolve(String toolName);
}使用此方法时:
-
在客户端,你向
ChatClient或ChatModel提供工具名称而非ToolCallback实例。 -
在服务端,
ToolCallbackResolver实现负责将工具名称解析为对应的ToolCallback实例。
默认情况下,Spring AI 使用 DelegatingToolCallbackResolver,它将工具解析委托给一系列 ToolCallbackResolver 实例:
-
SpringBeanToolCallbackResolver从类型为Function、Supplier、Consumer或BiFunction的 Spring Bean 中解析工具。详见 “[_dynamic_specification_bean]” 章节。 -
StaticToolCallbackResolver从静态的ToolCallback实例列表中解析工具。使用 Spring Boot 自动配置时,该解析器会自动配置应用上下文中所有ToolCallback类型的 Bean。
若使用 Spring Boot 自动配置,您可通过提供自定义的 ToolCallbackResolver Bean 来定制解析逻辑。
@Bean
ToolCallbackResolver toolCallbackResolver(List<FunctionCallback> toolCallbacks) {
StaticToolCallbackResolver staticToolCallbackResolver = new StaticToolCallbackResolver(toolCallbacks);
return new DelegatingToolCallbackResolver(List.of(staticToolCallbackResolver));
}ToolCallbackResolver 由 ToolCallingManager 内部使用,用于在运行时动态解析工具,同时支持 “[_framework_controlled_tool_execution]” 和 “[_user_controlled_tool_execution]” 两种模式。
可观测性
工具调用包含可观测性支持,通过 spring.ai.tool 观测项记录完成时间并传播追踪信息。详见 “Tool Calling Observability”。
(可选)Spring AI 可将工具调用参数和结果导出为 span 属性,默认因敏感性考虑处于禁用状态。详见 “工具调用参数与结果数据”。

