Spring 配置 Kafka 死信队列
1、简介
本文将带你了解如何在 Spring 中为 Apache Kafka 配置死信队列。
2、死信队列
死信队列(Dead Letter Queue,DLQ)用于存储由于各种原因无法正确处理的消息,例如间歇性系统故障、无效的消息模式或损坏的内容。这些消息可以稍后从 DLQ 中移除,以进行分析或重新处理。
下图是 DLQ 机制的简化流程:
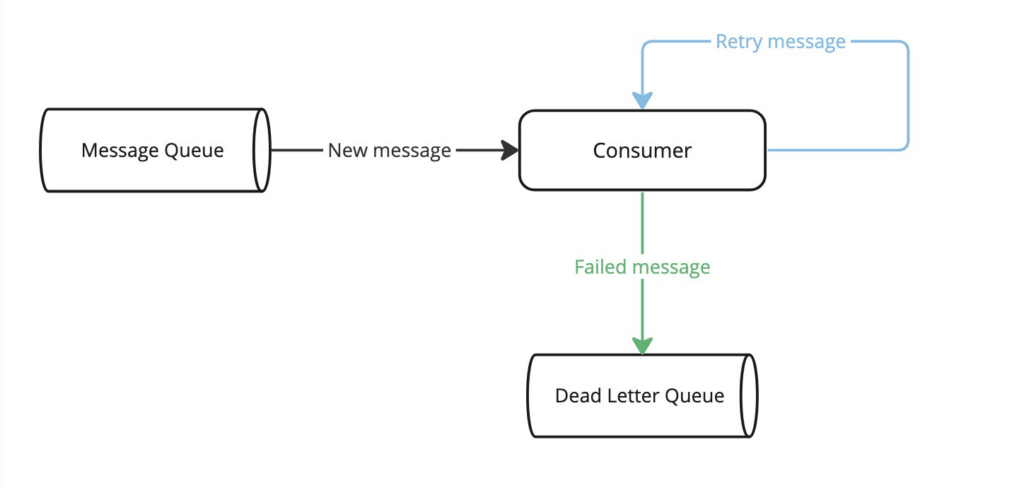
通常情况下,使用 DLQ 是一个不错的主意,但也有一些情况下应该避免使用 DLQ。例如,在对消息的精确顺序很重要的队列中,不建议使用 DLQ,因为重新处理 DLQ 消息会打乱消息的到达顺序。
3、Spring Kafka 中的死信队列
在 Spring Kafka 中,与 DLQ 概念相对应的是死信 Topic(DLT)。
接下来,我们通过一个简单的支付系统来介绍 DLT 应该如何使用。
3.1、Model 类
从 Model 类开始:
public class Payment {
private String reference;
private BigDecimal amount;
private Currency currency;
// Get、Set 方法省略
}
再实现一个用于创建事件的方法:
static Payment createPayment(String reference) {
Payment payment = new Payment();
payment.setAmount(BigDecimal.valueOf(71));
payment.setCurrency(Currency.getInstance("GBP"));
payment.setReference(reference);
return payment;
}
3.2、设置
接下来,添加 spring-kafka 和 jackson-databind 依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
<version>2.9.13</version> </dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.14.3</version>
</dependency>
创建 ConsumerFactory 和 ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory Bean:
@Bean
public ConsumerFactory<String, Payment> consumerFactory() {
Map<String, Object> config = new HashMap<>();
config.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, bootstrapServers);
return new DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory<>(
config, new StringDeserializer(), new JsonDeserializer<>(Payment.class));
}
@Bean
public ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<String, Payment> containerFactory() {
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<String, Payment> factory =
new ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<>();
factory.setConsumerFactory(consumerFactory());
return factory;
}
最后,实现 main Topic 的消费者:
@KafkaListener(topics = { "payments" }, groupId = "payments")
public void handlePayment(
Payment payment, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
log.info("Event on main topic={}, payload={}", topic, payment);
}
3.3、关闭重试
在实际项目中,通常在将事件发送到 DLT 之前重试处理,以防出错。使用 Spring Kafka 提供的非阻塞重试机制可以轻松实现这一目标。
不过,在本文中,我们要关闭重试功能,以突出 DLT 机制。当 main Topic 的消费者处理失败时,事件将直接发布到 DLT。
首先,定义 producerFactory 和 retryableTopicKafkaTemplate Bean:
@Bean
public ProducerFactory<String, Payment> producerFactory() {
Map<String, Object> config = new HashMap<>();
config.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, bootstrapServers);
return new DefaultKafkaProducerFactory<>(
config, new StringSerializer(), new JsonSerializer<>());
}
@Bean
public KafkaTemplate<String, Payment> retryableTopicKafkaTemplate() {
return new KafkaTemplate<>(producerFactory());
}
现在,定义 main Topic 的消费者,而无需额外的重试,如前所述:
@RetryableTopic(attempts = "1", kafkaTemplate = "retryableTopicKafkaTemplate")
@KafkaListener(topics = { "payments"}, groupId = "payments")
public void handlePayment(
Payment payment, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
log.info("Event on main topic={}, payload={}", topic, payment);
}
@RetryableTopic 注解中的 attempts 属性表示将消息发送到 DLT 之前尝试的次数。
4、配置死信主题(DLT)
实现 DLT 消费者:
@DltHandler
public void handleDltPayment(
Payment payment, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
log.info("Event on dlt topic={}, payload={}", topic, payment);
}
带有 @DltHandler 注解的方法必须与带有 @KafkaListener 注解的方法放在同一个类中。
接下来,介绍在 Spring Kafka 中可用的三种 DLT 配置。并为每种策略使用专门的 topic 和消费者,以便于单独了解每个示例。
4.1、“Fail on Error” 策略
使用 FAIL_ON_ERROR 策略,可以配置 DLT 消费者在 DLT 处理失败时结束执行而不重试:
@RetryableTopic(
attempts = "1",
kafkaTemplate = "retryableTopicKafkaTemplate",
dltStrategy = DltStrategy.FAIL_ON_ERROR)
@KafkaListener(topics = { "payments-fail-on-error-dlt"}, groupId = "payments")
public void handlePayment(
Payment payment, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
log.info("Event on main topic={}, payload={}", topic, payment);
}
@DltHandler
public void handleDltPayment(
Payment payment, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
log.info("Event on dlt topic={}, payload={}", topic, payment);
}
@KafkaListener 消费者会读取来自 payments-fail-on-error-dlt Topic 的消息。
测试,当 main 消费者成功时,事件是否没有发布到 DLT 上:
@Test
public void whenMainConsumerSucceeds_thenNoDltMessage() throws Exception {
CountDownLatch mainTopicCountDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
doAnswer(invocation -> {
mainTopicCountDownLatch.countDown();
return null;
}).when(paymentsConsumer)
.handlePayment(any(), any());
kafkaProducer.send(TOPIC, createPayment("dlt-fail-main"));
assertThat(mainTopicCountDownLatch.await(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)).isTrue();
verify(paymentsConsumer, never()).handleDltPayment(any(), any());
}
再来看看当 main 消费者和 DLT 消费者都无法处理事件时会发生什么:
@Test
public void whenDltConsumerFails_thenDltProcessingStops() throws Exception {
CountDownLatch mainTopicCountDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
CountDownLatch dlTTopicCountDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);
doAnswer(invocation -> {
mainTopicCountDownLatch.countDown();
throw new Exception("Simulating error in main consumer");
}).when(paymentsConsumer)
.handlePayment(any(), any());
doAnswer(invocation -> {
dlTTopicCountDownLatch.countDown();
throw new Exception("Simulating error in dlt consumer");
}).when(paymentsConsumer)
.handleDltPayment(any(), any());
kafkaProducer.send(TOPIC, createPayment("dlt-fail"));
assertThat(mainTopicCountDownLatch.await(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)).isTrue();
assertThat(dlTTopicCountDownLatch.await(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)).isFalse();
assertThat(dlTTopicCountDownLatch.getCount()).isEqualTo(1);
}
在上述测试中,main 消费者处理了一次事件,而 DLT 消费者只处理了一次。
4.2、DLT 重试
可以使用 ALWAYS_RETRY_ON_ERROR 策略,配置 DLT 消费者在 DLT 处理失败时尝试重新处理事件。这是默认使用的策略:
@RetryableTopic(
attempts = "1",
kafkaTemplate = "retryableTopicKafkaTemplate",
dltStrategy = DltStrategy.ALWAYS_RETRY_ON_ERROR)
@KafkaListener(topics = { "payments-retry-on-error-dlt"}, groupId = "payments")
public void handlePayment(
Payment payment, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
log.info("Event on main topic={}, payload={}", topic, payment);
}
@DltHandler
public void handleDltPayment(
Payment payment, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
log.info("Event on dlt topic={}, payload={}", topic, payment);
}
@KafkaListener 消费者会读取来自 payments-retry-on-error-dlt Topic 的消息。
接下来,测试当 main 和 DLT 消费者无法处理事件时会发生什么:
@Test
public void whenDltConsumerFails_thenDltConsumerRetriesMessage() throws Exception {
CountDownLatch mainTopicCountDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
CountDownLatch dlTTopicCountDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(3);
doAnswer(invocation -> {
mainTopicCountDownLatch.countDown();
throw new Exception("Simulating error in main consumer");
}).when(paymentsConsumer)
.handlePayment(any(), any());
doAnswer(invocation -> {
dlTTopicCountDownLatch.countDown();
throw new Exception("Simulating error in dlt consumer");
}).when(paymentsConsumer)
.handleDltPayment(any(), any());
kafkaProducer.send(TOPIC, createPayment("dlt-retry"));
assertThat(mainTopicCountDownLatch.await(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)).isTrue();
assertThat(dlTTopicCountDownLatch.await(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)).isTrue();
assertThat(dlTTopicCountDownLatch.getCount()).isEqualTo(0);
}
不出所料,DLT 消费者会尝试重新处理该事件。
4.3、禁用 DLT
也可以使用 NO_DLT 策略关闭 DLT 机制:
@RetryableTopic(
attempts = "1",
kafkaTemplate = "retryableTopicKafkaTemplate",
dltStrategy = DltStrategy.NO_DLT)
@KafkaListener(topics = { "payments-no-dlt" }, groupId = "payments")
public void handlePayment(
Payment payment, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
log.info("Event on main topic={}, payload={}", topic, payment);
}
@DltHandler
public void handleDltPayment(
Payment payment, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
log.info("Event on dlt topic={}, payload={}", topic, payment);
}
@KafkaListener 消费者从 payments-no-dlt Topic 中读取消息。
测试,当 main Topic 上的消费者无法处理事件时,该事件是否会被转发到 DLT:
@Test
public void whenMainConsumerFails_thenDltConsumerDoesNotReceiveMessage() throws Exception {
CountDownLatch mainTopicCountDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
CountDownLatch dlTTopicCountDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
doAnswer(invocation -> {
mainTopicCountDownLatch.countDown();
throw new Exception("Simulating error in main consumer");
}).when(paymentsConsumer)
.handlePayment(any(), any());
doAnswer(invocation -> {
dlTTopicCountDownLatch.countDown();
return null;
}).when(paymentsConsumer)
.handleDltPayment(any(), any());
kafkaProducer.send(TOPIC, createPayment("no-dlt"));
assertThat(mainTopicCountDownLatch.await(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)).isTrue();
assertThat(dlTTopicCountDownLatch.await(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)).isFalse();
assertThat(dlTTopicCountDownLatch.getCount()).isEqualTo(1);
}
不出所料,虽然实现了一个注解为 @DltHandler 的消费者,但事件并没有被转发到 DLT。
5、总结
本文介绍了三种不同的 DLT 策略。第一种是 FAIL_ON_ERROR 策略,在这种情况下,DLT 消费者不会尝试在发生故障时重新处理某个事件。相比之下,ALWAYS_RETRY_ON_ERROR 策略可确保 DLT 消费者在发生故障时尝试重新处理事件。在没有明确设置其他策略的情况下,这是默认使用的值。最后一种是 NO_DLT 策略,它可以完全关闭 DLT 机制。
Ref:https://www.baeldung.com/kafka-spring-dead-letter-queue

